Single-Stranded DNA Gap Accumulation Is a Functional Biomarker for USP1 Inhibitor Sensitivity
- PMID: 38885312
- PMCID: PMC11474172
- DOI: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-23-4007
Single-Stranded DNA Gap Accumulation Is a Functional Biomarker for USP1 Inhibitor Sensitivity
Abstract
Recent studies suggest that PARP and POLQ inhibitors confer synthetic lethality in BRCA1-deficient tumors by accumulation of single-stranded DNA (ssDNA) gaps at replication forks. Loss of USP1, a deubiquitinating enzyme, is also synthetically lethal with BRCA1 deficiency, and USP1 inhibitors are now undergoing clinical development for these cancers. Herein, we show that USP1 inhibitors also promote the accumulation of ssDNA gaps during replication in BRCA1-deficient cells, and this phenotype correlates with drug sensitivity. USP1 inhibition increased monoubiquitinated proliferating cell nuclear antigen at replication forks, mediated by the ubiquitin ligase RAD18, and knockdown of RAD18 caused USP1 inhibitor resistance and suppression of ssDNA gaps. USP1 inhibition overcame PARP inhibitor resistance in a BRCA1-mutated xenograft model and induced ssDNA gaps. Furthermore, USP1 inhibition was synergistic with PARP and POLQ inhibition in BRCA1-mutant cells, with enhanced ssDNA gap accumulation. Finally, in patient-derived ovarian tumor organoids, sensitivity to USP1 inhibition alone or in combination correlated with the accumulation of ssDNA gaps. Assessment of ssDNA gaps in ovarian tumor organoids represents a rapid approach for predicting response to USP1 inhibition in ongoing clinical trials. Significance: USP1 inhibitors kill BRCA1-deficient cells and cause ssDNA gap accumulation, supporting the potential of using ssDNA gap detection as a functional biomarker for clinical trials on USP1 inhibitors.
©2024 The Authors; Published by the American Association for Cancer Research.
Conflict of interest statement
J. Liu reports personal fees from AstraZeneca, Bristol Myers Squibb, Clovis Oncology, Daiichi Sankyo, Eisai, Genentech/Roche, GlaxoSmithKline, Regeneron Therapeutics, Revolution Medicine, Zentalis Pharmaceuticals, and Deciphera Pharmaceuticals outside the submitted work and institutional funding for clinical trials from 2X Oncology, Aravive, Arch Oncology, AstraZeneca, Bristol Myers Squibb, Clovis Oncology, GlaxoSmithKline, Impact Therapeutics, Regeneron, Seagen, Vigeo Therapeutics, and Zentalis Pharmaceuticals. G.I. Shapiro reports grants from Tango Therapeutics during the conduct of the study; grants and personal fees from Merck KGaA/EMD Serono; and grants from Bristol Myers Squibb, Merck & Co., Pfizer, Eli Lilly, Bicycle Therapeutics, Kymera Therapeutics, ImmunoMet, Concarlo Therapeutics, Janssen, and Xinthera outside the submitted work, as well as having a patent for Dosage regimen for sapacitabine and seliciclib, Cyclacel Therapeutics, and Compositions and methods for predicting response and resistance to CDK4/6 inhibition issued. L. Cornell has a patent for Dosage regimen for sapacitabine and seliciclib, Cyclacel Therapeutics, and Compositions and methods for predicting response and resistance to CDK4/6 inhibition issued. A.D. D’Andrea reports grants from Bristol Myers Squibb, EMD Serono, Moderna, and Tango Therapeutics; personal fees and other support from Impact Therapeutics, PrimeFour Therapeutics, and Covant Therapeutics; and personal fees from Servier Bio-Innovation LLC outside the submitted work. No disclosures were reported by the other authors.
Figures
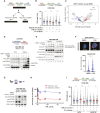
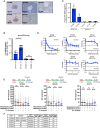

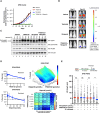
References
-
- Farmer H, McCabe N, Lord CJ, Tutt ANJ, Johnson DA, Richardson TB, et al. . Targeting the DNA repair defect in BRCA mutant cells as a therapeutic strategy. Nature 2005;434:917–21. - PubMed
-
- Bryant HE, Schultz N, Thomas HD, Parker KM, Flower D, Lopez E, et al. . Specific killing of BRCA2-deficient tumours with inhibitors of poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase. Nature 2005;434:913–7. - PubMed
-
- Ledermann J, Harter P, Gourley C, Friedlander M, Vergote I, Rustin G, et al. . Olaparib maintenance therapy in platinum-sensitive relapsed ovarian cancer. N Engl J Med 2012;366:1382–92. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

