Interaction between MED12 and ΔNp63 activates basal identity in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma
- PMID: 38886586
- PMCID: PMC11438066
- DOI: 10.1038/s41588-024-01790-y
Interaction between MED12 and ΔNp63 activates basal identity in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma
Abstract
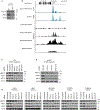
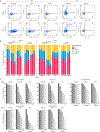
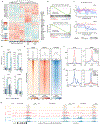
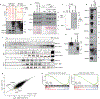
The presence of basal lineage characteristics signifies hyperaggressive human adenocarcinomas of the breast, bladder and pancreas. However, the biochemical mechanisms that maintain this aberrant cell state are poorly understood. Here we performed marker-based genetic screens in search of factors needed to maintain basal identity in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (PDAC). This approach revealed MED12 as a powerful regulator of the basal cell state in this disease. Using biochemical reconstitution and epigenomics, we show that MED12 carries out this function by bridging the transcription factor ΔNp63, a known master regulator of the basal lineage, with the Mediator complex to activate lineage-specific enhancer elements. Consistent with this finding, the growth of basal-like PDAC is hypersensitive to MED12 loss when compared to PDAC cells lacking basal characteristics. Taken together, our genetic screens have revealed a biochemical interaction that sustains basal identity in human cancer, which could serve as a target for tumor lineage-directed therapeutics.
© 2024. The Author(s), under exclusive licence to Springer Nature America, Inc.
Figures





Update of
-
Marker-based CRISPR screening reveals a MED12-p63 interaction that activates basal identity in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2023 Oct 27:2023.10.24.563848. doi: 10.1101/2023.10.24.563848. bioRxiv. 2023. Update in: Nat Genet. 2024 Jul;56(7):1377-1385. doi: 10.1038/s41588-024-01790-y. PMID: 37961243 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
References
METHODS-ONLY REFERENCES
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- F30 CA265134/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- T32 GM008759/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- F31 CA278591/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG069727/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P30 CA045508/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA248158/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P01 CA013106/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R35 GM139550/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- CA013106-Project 1/U.S. Department of Health & Human Services | NIH | National Cancer Institute (NCI)
- R01 CA229699/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA284630/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

