Problem-Based Learning in Medical Education: A Global Research Landscape of the Last Ten Years (2013-2022)
- PMID: 38887406
- PMCID: PMC11180071
- DOI: 10.1007/s40670-024-02003-1
Problem-Based Learning in Medical Education: A Global Research Landscape of the Last Ten Years (2013-2022)
Abstract
Background: Problem-based learning (PBL) constructs a curriculum that merges theory and practice by employing clinical scenarios or real-world problems. Originally designed for the pre-clinical phase of undergraduate medicine, PBL has since been integrated into diverse aspects of medical education. Therefore, this study aims to map the global scientific landscape related to PBL in medical education in the last ten years.
Methods: We combined bibliometrics and network analysis to analyze the metadata of related research articles published between 2013 and 2022 and indexed in the Web of Science Core Collection.
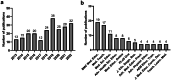
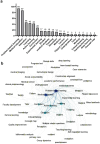
Results: Our results show an annual publication rate of 9.42%. The two main journals disseminating research on this subject are BMC Medical Education and Medical Teacher. Education & Educational Research and Health Care Sciences & Services are the two most frequent research areas, and also the two most central nodes of the related network. The USA and China are the most publishing countries, while the Netherlands and Canada are the most collaborative. The Maastricht University holds the position of most publishing and collaborative research organization. The University of California ranks second in publications, while the University of Toronto is the second most central research organization.
Conclusions: Our study provides an overview of the last ten years of publications related to PBL and medical education, and we hope it can be of interest to educators, researchers, and students involved with this subject.
Supplementary information: The online version contains supplementary material available at 10.1007/s40670-024-02003-1.
Keywords: Bibliometrics; Medical education; Network analysis; Problem-based learning; Scientific publication.
© The Author(s) under exclusive licence to International Association of Medical Science Educators 2024. Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing InterestsThe authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


References
-
- Schmidt HG. One-day, one-problem. Singapore: Springer Singapore; 2012. A brief history of problem-based learning; pp. 21–40.
-
- Hillen H, Scherpbier A, Wijnen W. History of problem-based learning in medical education. In: van Berkel H, Scherpbier A, Hillen H, van der Vleuten C, editors. Lessons from problem-based learning. OUP Oxford; 2010. pp. 5–11.
-
- Servant-Miklos VFC. A revolution in its own right: how Maastricht University reinvented problem-based learning. Health Prof Educ. 2019;5:283–93. doi: 10.1016/j.hpe.2018.12.005. - DOI
-
- Servant-Miklos VFC, Norman GR, Schmidt HG. The Wiley handbook of problem-based learning. Wiley. -: -; 2019. A short intellectual history of problem-based learning; pp. 3–24.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
