Ferrostatin-1 inhibits fibroblast fibrosis in keloid by inhibiting ferroptosis
- PMID: 38887622
- PMCID: PMC11182022
- DOI: 10.7717/peerj.17551
Ferrostatin-1 inhibits fibroblast fibrosis in keloid by inhibiting ferroptosis
Abstract
Background: Keloid is a chronic proliferative fibrotic disease caused by abnormal fibroblasts proliferation and excessive extracellular matrix (ECM) production. Numerous fibrotic disorders are significantly influenced by ferroptosis, and targeting ferroptosis can effectively mitigate fibrosis development. This study aimed to investigate the role and mechanism of ferroptosis in keloid development.
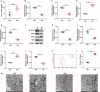
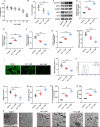
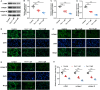
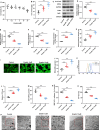
Methods: Keloid tissues from keloid patients and normal skin tissues from healthy controls were collected. Iron content, lipid peroxidation (LPO) level, and the mRNA and protein expression of ferroptosis-related genes including solute carrier family 7 member 11 (SLC7A11), glutathione peroxidase 4 (GPX4), transferrin receptor (TFRC), and nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor 2 (Nrf2) were determined. Mitochondrial morphology was observed using transmission electron microscopy (TEM). Keloid fibroblasts (KFs) were isolated from keloid tissues, and treated with ferroptosis inhibitor ferrostatin-1 (fer-1) or ferroptosis activator erastin. Iron content, ferroptosis-related marker levels, LPO level, mitochondrial membrane potential, ATP content, and mitochondrial morphology in KFs were detected. Furthermore, the protein levels of α-smooth muscle actin (α-SMA), collagen I, and collagen III were measured to investigate whether ferroptosis affect fibrosis in KFs.
Results: We found that iron content and LPO level were substantially elevated in keloid tissues and KFs. SLC7A11, GPX4, and Nrf2 were downregulated and TFRC was upregulated in keloid tissues and KFs. Mitochondria in keloid tissues and KFs exhibited ferroptosis-related pathology. Fer-1 treatment reduced iron content, restrained ferroptosis and mitochondrial dysfunction in KFs, Moreover, ferrostatin-1 restrained the protein expression of α-SMA, collagen I, and collagen III in KFs. Whereas erastin treatment showed the opposite results.
Conclusion: Ferroptosis exists in keloid. Ferrostatin-1 restrained ECM deposition and fibrosis in keloid through inhibiting ferroptosis, and erastin induced ECM deposition and fibrosis through intensifying ferroptosis.
Keywords: Erastin; Ferroptosis; Ferrostatin-1; Fibroblasts; Fibrosis; Keloid.
©2024 Yang et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare there are no competing interests.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Lipid Peroxidation, GSH Depletion, and SLC7A11 Inhibition Are Common Causes of EMT and Ferroptosis in A549 Cells, but Different in Specific Mechanisms.DNA Cell Biol. 2021 Feb;40(2):172-183. doi: 10.1089/dna.2020.5730. Epub 2020 Dec 22. DNA Cell Biol. 2021. PMID: 33351681
-
Cadmium Inhibits Proliferation of Human Bronchial Epithelial BEAS-2B Cells Through Inducing Ferroptosis via Targeted Regulation of the Nrf2/SLC7A11/GPX4 Pathway.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 Jul 25;26(15):7204. doi: 10.3390/ijms26157204. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 40806353 Free PMC article.
-
Nrf2 alleviates acute ischemic stroke induced ferroptosis via regulating xCT/GPX4 pathway.Free Radic Biol Med. 2025 Apr;231:153-162. doi: 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2025.02.040. Epub 2025 Feb 26. Free Radic Biol Med. 2025. PMID: 40020881
-
Lipid Peroxidation-Dependent Cell Death Regulated by GPx4 and Ferroptosis.Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 2017;403:143-170. doi: 10.1007/82_2016_508. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 2017. PMID: 28204974 Review.
-
Ferroptosis and renal fibrosis: mechanistic insights and emerging therapeutic targets.Ren Fail. 2025 Dec;47(1):2498629. doi: 10.1080/0886022X.2025.2498629. Epub 2025 May 6. Ren Fail. 2025. PMID: 40329437 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Ferroptosis in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis: mechanisms, impact, and therapeutic opportunities.Front Immunol. 2025 May 21;16:1567994. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2025.1567994. eCollection 2025. Front Immunol. 2025. PMID: 40469306 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Unveiling ferroptosis: a new frontier in skin disease research.Front Immunol. 2024 Oct 4;15:1485523. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1485523. eCollection 2024. Front Immunol. 2024. PMID: 39430757 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Skin Aging and the Upcoming Role of Ferroptosis in Geroscience.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Jul 28;25(15):8238. doi: 10.3390/ijms25158238. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39125810 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Increased melanin induces aberrant keratinocyte - melanocyte - basal - fibroblast cell communication and fibrogenesis by inducing iron overload and ferroptosis resistance in keloids.Cell Commun Signal. 2025 Mar 18;23(1):141. doi: 10.1186/s12964-025-02116-z. Cell Commun Signal. 2025. PMID: 40102920 Free PMC article.
-
Orthogonal upconversion supramolecular microneedles promote endogenous ferroptosis in keloids.Theranostics. 2025 May 8;15(13):6184-6202. doi: 10.7150/thno.108289. eCollection 2025. Theranostics. 2025. PMID: 40521195 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Cheng H, Feng D, Li X, Gao L, Tang S, Liu W, Wu X, Yue S, Li C, Luo Z. Iron deposition-induced ferroptosis in alveolar type II cells promotes the development of pulmonary fibrosis. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta: Molecular Basis of Disease. 2021;1867(12):166204. doi: 10.1016/j.bbadis.2021.166204. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

