Circ_0007386 Promotes the Progression of Hepatocellular Carcinoma Through the miR-507/ CCNT2 Axis
- PMID: 38887684
- PMCID: PMC11182359
- DOI: 10.2147/JHC.S459633
Circ_0007386 Promotes the Progression of Hepatocellular Carcinoma Through the miR-507/ CCNT2 Axis
Abstract
Background: Circular RNAs (circRNAs) have been shown to play a crucial role in the initiation and development of Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). However, the mechanism and function of circ_0007386 in HCC are still unknown.
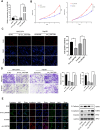
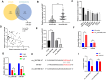
Methods: Circ_0007386 expression level in HCC tissues, and HCC cell lines was further analyzed by qRT-PCR. Agarose gel electrophoresis and Sanger sequencing were used to figure out the structure of circ_0007386. The involvement of circ_0007386 in HCC development was evaluated by experimental investigations conducted in both laboratory settings (in vitro) and living organisms (in vivo). RNA immunoprecipitation, Western blotting, luciferase reporter assay and fluorescence in situ hybridization (FISH) were applied for finding out the interaction among circ_0007386, miR-507 and CCNT2. To assess the connection between circ_0007386 and lenvatinib resistance, lenvatinib-resistant HCC cell lines were employed.
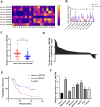
Results: The expression of circ_0007386 was found to increase in HCC tissues, and it was observed to be associated with a worse prognosis. Overexpression of circ_0007386 stimulated HCC cells proliferation, invasion, migration and the epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT) while silencing of circ_0007386 resulted in the opposite effect. Mechanistic investigations revealed that circ_0007386 acted as a competing endogenous RNA of miR-507 to prevent CCNT2 downregulation. Downregulating miR-507 or overexpressing CCNT2 could reverse phenotypic alterations that originated from inhibiting of circ_0007386. Importantly, circ_0007386 determines the resistance of hepatoma cells to lenvatinib treatment.
Conclusion: Circ_0007386 advanced HCC progression and lenvatinib resistance through the miR-507/ CCNT2 axis. Meanwhile, circ_0007386 served as a potential biomarker and therapeutic target in HCC patients.
Keywords: CCNT2; Lenvatinib; circ_0007386; hepatocellular carcinoma; miR-507.
© 2024 Feng et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors report no conflicts of interest in this work.
Figures






Similar articles
-
Nanoparticles Mediated circROBO1 Silencing to Inhibit Hepatocellular Carcinoma Progression by Modulating miR-130a-5p/CCNT2 Axis.Int J Nanomedicine. 2023 Mar 30;18:1677-1693. doi: 10.2147/IJN.S399318. eCollection 2023. Int J Nanomedicine. 2023. PMID: 37020690 Free PMC article.
-
Silencing of hsa_circ_0101145 reverses the epithelial-mesenchymal transition in hepatocellular carcinoma via regulation of the miR-548c-3p/LAMC2 axis.Aging (Albany NY). 2020 Jun 18;12(12):11623-11635. doi: 10.18632/aging.103324. Epub 2020 Jun 18. Aging (Albany NY). 2020. PMID: 32554866 Free PMC article.
-
Circular RNA circ_0001459 accelerates hepatocellular carcinoma progression via the miR-6165/IGF1R axis.Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2022 Jun;1512(1):46-60. doi: 10.1111/nyas.14753. Epub 2022 Feb 23. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2022. PMID: 35199365 Free PMC article.
-
Circular RNA hsa_circ_0003288 induces EMT and invasion by regulating hsa_circ_0003288/miR-145/PD-L1 axis in hepatocellular carcinoma.Cancer Cell Int. 2021 Apr 15;21(1):212. doi: 10.1186/s12935-021-01902-2. Cancer Cell Int. 2021. PMID: 33858418 Free PMC article.
-
Circ-CSPP1 knockdown suppresses hepatocellular carcinoma progression through miR-493-5p releasing-mediated HMGB1 downregulation.Cell Signal. 2021 Oct;86:110065. doi: 10.1016/j.cellsig.2021.110065. Epub 2021 Jun 26. Cell Signal. 2021. PMID: 34182091 Review.
Cited by
-
Exosome-derived hsa_circ_0007132 promotes lenvatinib resistance by inhibiting the ubiquitin-mediated degradation of NONO.Noncoding RNA Res. 2025 May 15;14:1-13. doi: 10.1016/j.ncrna.2025.05.007. eCollection 2025 Oct. Noncoding RNA Res. 2025. PMID: 40521241 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

