Stress-induced Rab11a-exosomes induce amphiregulin-mediated cetuximab resistance in colorectal cancer
- PMID: 38887984
- PMCID: PMC11184284
- DOI: 10.1002/jev2.12465
Stress-induced Rab11a-exosomes induce amphiregulin-mediated cetuximab resistance in colorectal cancer
Erratum in
-
Correction to "Stress-Induced Rab11a-Exosomes Induce Amphiregulin-Mediated Cetuximab Resistance in Colorectal Cancer".J Extracell Vesicles. 2025 May;14(5):e70081. doi: 10.1002/jev2.70081. J Extracell Vesicles. 2025. PMID: 40314086 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
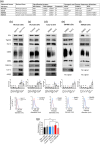
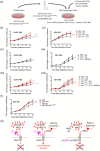
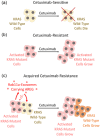
Exosomes are secreted vesicles made intracellularly in the endosomal system. We have previously shown that exosomes are not only made in late endosomes, but also in recycling endosomes marked by the monomeric G-protein Rab11a. These vesicles, termed Rab11a-exosomes, are preferentially secreted under nutrient stress from several cancer cell types, including HCT116 colorectal cancer (CRC) cells. HCT116 Rab11a-exosomes have particularly potent signalling activities, some mediated by the epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) ligand, amphiregulin (AREG). Mutant activating forms of KRAS, a downstream target of EGFR, are often found in advanced CRC. When absent, monoclonal antibodies, such as cetuximab, which target the EGFR and block the effects of EGFR ligands, such as AREG, can be administered. Patients, however, inevitably develop resistance to cetuximab, either by acquiring KRAS mutations or via non-genetic microenvironmental changes. Here we show that nutrient stress in several CRC cell lines causes the release of AREG-carrying Rab11a-exosomes. We demonstrate that while soluble AREG has no effect, much lower levels of AREG bound to Rab11a-exosomes from cetuximab-resistant KRAS-mutant HCT116 cells, can suppress the effects of cetuximab on KRAS-wild type Caco-2 CRC cells. Using neutralising anti-AREG antibodies and an intracellular EGFR kinase inhibitor, we show that this effect is mediated via AREG activation of EGFR, and not transfer of activated KRAS. Therefore, presentation of AREG on Rab11a-exosomes affects its ability to compete with cetuximab. We propose that this Rab11a-exosome-mediated mechanism contributes to the establishment of resistance in cetuximab-sensitive cells and may explain why in cetuximab-resistant tumours only some cells carry mutant KRAS.
Keywords: AREG; EGFR; Rab11a‐exosome; cetuximab; colorectal cancer; extracellular vesicle.
© 2024 The Author(s). Journal of Extracellular Vesicles published by Wiley Periodicals LLC on behalf of International Society for Extracellular Vesicles.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest in relation to this work.
Figures

References
-
- Allegra, C. J. , Rumble, R. B. , Hamilton, S. R. , Mangu, P. B. , Roach, N. , Hantel, A. , & Schilsky, R. L. (2016). Extended RAS gene mutation testing in metastatic colorectal carcinoma to predict response to anti‐epidermal growth factor receptor monoclonal antibody therapy: American Society of Clinical Oncology Provisional Clinical Opinion Update 2015. Journal of Clinical Oncology, 34, 179–185. - PubMed
-
- Bando, H. , Ohtsu, A. , & Yoshino, T. (2023). Therapeutic landscape and future direction of metastatic colorectal cancer. Nature Reviews Gastroenterology & Hepatology, 20, 306–322. - PubMed
-
- Bhattacharya, S. (2023). An empirical review on the resistance mechanisms of epidermal growth factor receptor inhibitors and predictive molecular biomarkers in colorectal cancer. Critical Reviews in Oncology/Hematology, 183, 103916. - PubMed
-
- Bishop, P. C. , Myers, T. , Robey, R. , Fry, D. W. , Liu, E. T. , Blagosklonny, M. V. , & Bates, S. E. (2002). Differential sensitivity of cancer cells to inhibitors of the epidermal growth factor receptor family. Oncogene, 21, 119–127. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

