Plasma pTau181 Reveals a Pathological Signature that Predicts Cognitive Outcomes in Lewy Body Disease
- PMID: 38888142
- PMCID: PMC11324388
- DOI: 10.1002/ana.27003
Plasma pTau181 Reveals a Pathological Signature that Predicts Cognitive Outcomes in Lewy Body Disease
Abstract
Objective: To determine whether plasma phosphorylated-Tau181 (pTau181) could be used as a diagnostic biomarker of concurrent Alzheimer's disease neuropathologic change (ADNC) or amyloidosis alone, as well as a prognostic, monitoring, and susceptibility/risk biomarker for clinical outcomes in Lewy body disease (LBD).
Methods: We studied 565 participants: 94 LBD with normal cognition, 83 LBD with abnormal cognition, 114 with Alzheimer's disease, and 274 cognitively normal. Plasma pTau181 levels were measured with the Lumipulse G platform. Diagnostic accuracy for concurrent ADNC and amyloidosis was assessed with Receiver Operating Characteristic curves in a subset of participants with CSF pTau181/Aβ42, and CSF Aβ42/Aβ40 or amyloid-β PET, respectively. Linear mixed effects models were used to examine the associations between baseline and longitudinal plasma pTau181 levels and clinical outcomes.
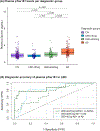
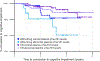
Results: Plasma pTau181 predicted concurrent ADNC and amyloidosis in LBD with abnormal cognition with 87% and 72% accuracy, respectively. In LBD patients with abnormal cognition, higher baseline plasma pTau181 was associated with worse baseline MoCA and CDR-SB, as well as accelerated decline in CDR-SB. Additionally, in this group, rapid increases in plasma pTau181 over 3 years predicted a faster decline in CDR-SB and memory. In LBD patients with normal cognition, there was no association between baseline or longitudinal plasma pTau181 levels and clinical outcomes; however, elevated pTau181 at baseline increased the risk of conversion to cognitive impairment.
Interpretation: Our findings suggest that plasma pTau181 is a promising biomarker for concurrent ADNC and amyloidosis in LBD. Furthermore, plasma pTau181 holds potential as a prognostic, monitoring, and susceptibility/risk biomarker, predicting disease progression in LBD. ANN NEUROL 2024;96:526-538.
© 2024 The Author(s). Annals of Neurology published by Wiley Periodicals LLC on behalf of American Neurological Association.
Conflict of interest statement
Potential Conflicts of Interest
Nothing to report.
Figures
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- U24 AG021886/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AG066515/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- NS075097/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R21 AG058859/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01NS115114/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R21AG058859/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- K99AG071837/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- P50 NS062684/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- RF1AG077443/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P50 AG047366/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 NS115114/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- NS062684/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- F32AG074625/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P30-AG066515/National Alzheimer's Coordinating Center
- F32 AG074625/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- 6440.0/Michael J. Fox Foundation for Parkinson's Research
- K99 AG071837/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- RF1 AG077443/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG074339/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- AARFD-21-849349/ALZ/Alzheimer's Association/United States
- K23 NS075097/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- AG047366/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

