Airborne Aluminum as an Underestimated Source of Human Exposure: Quantification of Aluminum in 24 Human Tissue Types Reveals High Aluminum Concentrations in Lung and Hilar Lymph Node Tissues
- PMID: 38888518
- PMCID: PMC11223461
- DOI: 10.1021/acs.est.4c01910
Airborne Aluminum as an Underestimated Source of Human Exposure: Quantification of Aluminum in 24 Human Tissue Types Reveals High Aluminum Concentrations in Lung and Hilar Lymph Node Tissues
Abstract
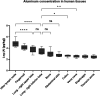
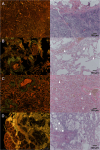
Aluminum (Al) is the most abundant metal in the earth's crust, and humans are exposed to Al through sources like food, cosmetics, and medication. So far, no comprehensive data on the Al distribution between and within human tissues were reported. We measured Al concentrations in 24 different tissue types of 8 autopsied patients using ICP-MS/MS (inductively coupled plasma-tandem mass spectrometry) under cleanroom conditions and found surprisingly high concentrations in both the upper and inferior lobes of the lung and hilar lymph nodes. Al/Si ratios in lung and hilar lymph node samples of 12 additional patients were similar to the ratios reported in urban fine dust. Histological analyses using lumogallion staining showed Al in lung erythrocytes and macrophages, indicating the uptake of airborne Al in the bloodstream. Furthermore, Al was continuously found in PM2.5 and PM10 fine dust particles over 7 years in Upper Austria, Austria. According to our findings, air pollution needs to be reconsidered as a major Al source for humans and the environment.
Keywords: ICP–MS; PM10–PM2.5; air pollution; aluminum; lumogallion; tissue distribution.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interest.
Figures
References
-
- Humphreys S.; Bolger P. M.. A Public Health Analysis of Dietary Aluminium. In Aluminium Toxicity in Infants’ Health and Disease; World Scientific, 1998; pp 226–237.
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

