A genetically-encoded fluorescence-based reporter to spatiotemporally investigate mannose-6-phosphate pathway
- PMID: 38888935
- PMCID: PMC11321044
- DOI: 10.1091/mbc.E23-09-0344
A genetically-encoded fluorescence-based reporter to spatiotemporally investigate mannose-6-phosphate pathway
Abstract
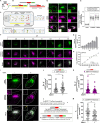
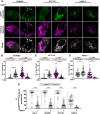
Maintenance of a pool of active lysosomes with acidic pH and degradative hydrolases is crucial for cell health. Abnormalities in lysosomal function are closely linked to diseases, such as lysosomal storage disorders, neurodegeneration, intracellular infections, and cancer among others. Emerging body of research suggests the malfunction of lysosomal hydrolase trafficking pathway to be a common denominator of several disease pathologies. However, available conventional tools to assess lysosomal hydrolase trafficking are insufficient and fail to provide a comprehensive picture about the trafficking flux and location of lysosomal hydrolases. To address some of the shortcomings, we designed a genetically-encoded fluorescent reporter containing a lysosomal hydrolase tandemly tagged with pH sensitive and insensitive fluorescent proteins, which can spatiotemporally trace the trafficking of lysosomal hydrolases. As a proof of principle, we demonstrate that the reporter can detect perturbations in hydrolase trafficking, that are induced by pharmacological manipulations and pathophysiological conditions like intracellular protein aggregates. This reporter can effectively serve as a probe for mapping the mechanistic intricacies of hydrolase trafficking pathway in health and disease and is a utilitarian tool to identify genetic and pharmacological modulators of this pathway, with potential therapeutic implications.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of Interests: The authors declare no financial conflict of interest.
Figures



Similar articles
-
LYSET/TMEM251/GCAF is critical for autophagy and lysosomal function by regulating the mannose-6-phosphate (M6P) pathway.Autophagy. 2023 May;19(5):1596-1598. doi: 10.1080/15548627.2023.2167375. Epub 2023 Jan 16. Autophagy. 2023. PMID: 36633445 Free PMC article.
-
A shortcut to the lysosome: the mannose-6-phosphate-independent pathway.Mol Genet Metab. 2012 Nov;107(3):257-66. doi: 10.1016/j.ymgme.2012.07.012. Epub 2012 Jul 20. Mol Genet Metab. 2012. PMID: 22884962 Review.
-
LYSET/TMEM251- a novel key component of the mannose 6-phosphate pathway.Autophagy. 2023 Jul;19(7):2143-2145. doi: 10.1080/15548627.2023.2167376. Epub 2023 Jan 22. Autophagy. 2023. PMID: 36633450 Free PMC article.
-
Targeted Analysis of Lysosomal Directed Proteins and Their Sites of Mannose-6-phosphate Modification.Mol Cell Proteomics. 2019 Jan;18(1):16-27. doi: 10.1074/mcp.RA118.000967. Epub 2018 Sep 20. Mol Cell Proteomics. 2019. PMID: 30237200 Free PMC article.
-
Mannose-6-phosphate pathway: a review on its role in lysosomal function and dysfunction.Mol Genet Metab. 2012 Apr;105(4):542-50. doi: 10.1016/j.ymgme.2011.12.012. Epub 2011 Dec 23. Mol Genet Metab. 2012. PMID: 22266136 Review.
References
-
- Anitei M, Chenna R, Czupalla C, Esner M, Christ S, Lenhard S, Korn K, Meyenhofer F, Bickle M, Zerial M, Hoflack B (2014). A high throughput siRNA screen identifies genes that regulate mannose 6-phosphate receptor trafficking. J Cell Sci 127, 5079–5092. - PubMed
-
- Ballabio A, Bonifacino JS (2020). Lysosomes as dynamic regulators of cell and organismal homeostasis. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 21, 101–118. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

