Identifying People at High Risk for Severe Aortic Stenosis: Aortic Valve Calcium Versus Lipoprotein(a) and Low-Density Lipoprotein Cholesterol
- PMID: 38889215
- PMCID: PMC11423705
- DOI: 10.1161/CIRCIMAGING.123.016372
Identifying People at High Risk for Severe Aortic Stenosis: Aortic Valve Calcium Versus Lipoprotein(a) and Low-Density Lipoprotein Cholesterol
Abstract
Background: Aortic valve calcification (AVC), Lp(a) [lipoprotein(a)], and low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-C) are associated with severe aortic stenosis (AS). We aimed to determine which of these risk factors were most strongly associated with the risk of incident severe AS.
Methods: A total of 6792 participants from the MESA study (Multi-Ethnic Study of Atherosclerosis) had computed tomography-quantified AVC, Lp(a), and LDL-C values at MESA visit 1 (2000-2002). We calculated the absolute event rate of incident adjudicated severe AS per 1000 person-years and performed multivariable adjusted Cox proportional hazards regression.
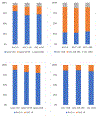
Results: The mean age was 62 years old, and 47% were women. Over a median 16.7-year follow-up, the rate of incident severe AS increased exponentially with higher AVC, regardless of Lp(a) or LDL-C values. Participants with AVC=0 had a very low rate of severe AS even with elevated Lp(a) ≥50 mg/dL (<0.1/1000 person-years) or LDL-C ≥130 mg/dL (0.1/1000 person-years). AVC >0 was strongly associated with severe AS when Lp(a) <50 mg/dL hazard ratio (HR) of 33.8 (95% CI, 16.4-70.0) or ≥50 mg/dL HR of 61.5 (95% CI, 7.7-494.2) and when LDL-C <130 mg/dL HR of 31.1 (95% CI, 14.4-67.1) or ≥130 mg/dL HR of 50.2 (95% CI, 13.2-191.9).
Conclusions: AVC better identifies people at high risk for severe AS compared with Lp(a) or LDL-C, and people with AVC=0 have a very low long-term rate of severe AS regardless of Lp(a) or LDL-C level. These results suggest AVC should be the preferred prognostic risk marker to identify patients at high risk for severe AS, which may help inform participant selection for future trials testing novel strategies to prevent severe AS.
Keywords: X-ray; aortic stenosis; aortic valve stenosis; computed tomography; lipoprotein(a); lipoproteins, LDL.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

References
-
- Pujari SH, Agasthi P. Aortic Stenosis. In: StatPearls. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing LLC; 2022. - PubMed
-
- Boakye E, Dardari Z, Obisesan OH, Osei AD, Wang FM, Honda Y, Dzaye O, Osuji N, Carr JJ, Howard-Claudio C, et al. Sex-and race-specific burden of aortic valve calcification among older adults without overt coronary heart disease: The Atherosclerosis Risk in Communities Study. Atherosclerosis. 2022; 355:68–75. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Osnabrugge RL, Mylotte D, Head SJ, Van Mieghem NM, Nkomo VT, LeReun CM, Bogers AJ, Piazza N, Kappetein AP. Aortic stenosis in the elderly: disease prevalence and number of candidates for transcatheter aortic valve replacement: a meta-analysis and modeling study. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2013; 62: 1002–1012. - PubMed
-
- Kearney LG, Ord M, Buxton BF, Matalanis G, Patel SK, Burrell LM, Srivastava PM. Progression of aortic stenosis in elderly patients over long-term follow up. Int J Cardiol. 2013; 167: 1226–1231. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Supplementary concepts
Grants and funding
- N01 HC095168/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- 75N92020D00001/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R21 HL150458/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC095167/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL146666/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201500003I/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR000040/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC095166/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC095160/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- 75N92020D00002/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201500003C/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL071739/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC095161/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- 75N92020D00005/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR001079/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC095169/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC095159/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- 75N92020D00003/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR001420/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- 75N92020D00004/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC095163/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- 75N92020D00007/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC095162/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- 75N92020D00006/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC095165/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC095164/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

