Epigenetic age acceleration in follicular fluid and markers of ovarian response among women undergoing IVF
- PMID: 38890131
- PMCID: PMC11373381
- DOI: 10.1093/humrep/deae136
Epigenetic age acceleration in follicular fluid and markers of ovarian response among women undergoing IVF
Abstract
Study question: Are markers of epigenetic age acceleration in follicular fluid associated with outcomes of ovarian stimulation?
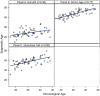
Summary answer: Increased epigenetic age acceleration of follicular fluid using the Horvath clock, but not other epigenetic clocks (GrimAge and Granulosa Cell), was associated with lower peak estradiol levels and decreased number of total and mature oocytes.
What is known already: In granulosa cells, there are inconsistent findings between epigenetic age acceleration and ovarian response outcomes.
Study design, size, duration: Our study included 61 women undergoing IVF at an academic fertility clinic in the New England area who were part of the Environment and Reproductive Health Study (2006-2016).
Participants/materials, setting, methods: Participants provided a follicular fluid sample during oocyte retrieval. DNA methylation of follicular fluid was assessed using a genome-wide methylation screening tool. Three established epigenetic clocks (Horvath, GrimAge, and Granulosa Cell) were used to predict DNA-methylation-based epigenetic age. To calculate the age acceleration, we regressed epigenetic age on chronological age and extracted the residuals. The association between epigenetic age acceleration and ovarian response outcomes (peak estradiol levels, follicle stimulation hormone, number of total, and mature oocytes) was assessed using linear and Poisson regression adjusted for chronological age, three surrogate variables (to account for cellular heterogeneity), race, smoking status, initial infertility diagnosis, and stimulation protocol.
Main results and role of chance: Compared to the median chronological age of our participants (34 years), the Horvath clock predicted, on an average, a younger epigenetic age (median: 24.2 years) while the GrimAge (median: 38.6 years) and Granulosa Cell (median: 39.0 years) clocks predicted, on an average, an older epigenetic age. Age acceleration based on the Horvath clock was associated with lower peak estradiol levels (-819.4 unit decrease in peak estradiol levels per standard deviation increase; 95% CI: -1265.7, -373.1) and fewer total (% change in total oocytes retrieved per standard deviation increase: -21.8%; 95% CI: -37.1%, -2.8%) and mature oocytes retrieved (% change in mature oocytes retrieved per standard deviation increase: -23.8%; 95% CI: -39.9%, -3.4%). The age acceleration based on the two other epigenetic clocks was not associated with markers of ovarian response.
Limitations, reasons for caution: Our sample size was small and we did not specifically isolate granulosa cells from follicular fluid samples so our samples could have included mixed cell types.
Wider implications of the findings: Our results highlight that certain epigenetic clocks may be predictive of ovarian stimulation outcomes when applied to follicular fluid; however, the inconsistent findings for specific clocks across studies indicate a need for further research to better understand the clinical utility of epigenetic clocks to improve IVF treatment.
Study funding/competing interest(s): The study was supported by grants ES009718, ES022955, ES000002, and ES026648 from the National Institute of Environmental Health Sciences (NIEHS) and a pilot grant from the NIEHS-funded HERCULES Center at Emory University (P30 ES019776). RBH was supported by the Emory University NIH Training Grant (T32-ES012870).
Trial registration number: N/A.
Keywords: GrimAge age acceleration; Horvath age acceleration; follicular fluid; granulosa cell age acceleration; ovarian response.
© The Author(s) 2024. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of European Society of Human Reproduction and Embryology. All rights reserved. For permissions, please email: journals.permissions@oup.com.
Conflict of interest statement
None declared.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Urinary bisphenol A concentrations and early reproductive health outcomes among women undergoing IVF.Hum Reprod. 2012 Dec;27(12):3583-92. doi: 10.1093/humrep/des328. Epub 2012 Sep 26. Hum Reprod. 2012. PMID: 23014629 Free PMC article.
-
Single-cell analysis comparing early-stage oocytes from fresh and slow-frozen/thawed human ovarian cortex reveals minimal impact of cryopreservation on the oocyte transcriptome.Hum Reprod. 2025 Apr 1;40(4):683-694. doi: 10.1093/humrep/deaf009. Hum Reprod. 2025. PMID: 39919251
-
The interplay between mitochondrial DNA genotypes, female infertility, ovarian response, and mutagenesis in oocytes.Hum Reprod Open. 2024 Dec 30;2025(1):hoae074. doi: 10.1093/hropen/hoae074. eCollection 2025. Hum Reprod Open. 2024. PMID: 39830711 Free PMC article.
-
The use of follicle flushing during oocyte retrieval in assisted reproductive technologies: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Hum Reprod. 2012 Aug;27(8):2373-9. doi: 10.1093/humrep/des174. Epub 2012 May 30. Hum Reprod. 2012. PMID: 22647450 Free PMC article.
-
Cycle cancellation and pregnancy after luteal estradiol priming in women defined as poor responders: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Hum Reprod. 2013 Nov;28(11):2981-9. doi: 10.1093/humrep/det306. Epub 2013 Jul 25. Hum Reprod. 2013. PMID: 23887073 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Christensen MW, Keefe DL, Wang F, Hansen CS, Chamani IJ, Sommer C, Nyegaard M, Rohde PD, Nielsen AL, Bybjerg-Grauholm J et al. Idiopathic early ovarian aging: is there a relation with premenopausal accelerated biological aging in young women with diminished response to ART? J Assist Reprod Genet 2021;38:3027–3038. 10.1007/s10815-021-02326-7. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

