Controlled enzymatic synthesis of oligonucleotides
- PMID: 38890393
- PMCID: PMC11189433
- DOI: 10.1038/s42004-024-01216-0
Controlled enzymatic synthesis of oligonucleotides
Abstract
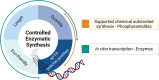
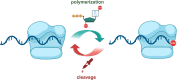
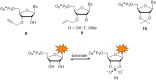
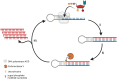
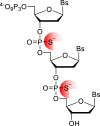
Oligonucleotides are advancing as essential materials for the development of new therapeutics, artificial genes, or in storage of information applications. Hitherto, our capacity to write (i.e., synthesize) oligonucleotides is not as efficient as that to read (i.e., sequencing) DNA/RNA. Alternative, biocatalytic methods for the de novo synthesis of natural or modified oligonucleotides are in dire need to circumvent the limitations of traditional synthetic approaches. This Perspective article summarizes recent progress made in controlled enzymatic synthesis, where temporary blocked nucleotides are incorporated into immobilized primers by polymerases. While robust protocols have been established for DNA, RNA or XNA synthesis is more challenging. Nevertheless, using a suitable combination of protected nucleotides and polymerase has shown promises to produce RNA oligonucleotides even though the production of long DNA/RNA/XNA sequences (>1000 nt) remains challenging. We surmise that merging ligase- and polymerase-based synthesis would help to circumvent the current shortcomings of controlled enzymatic synthesis.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

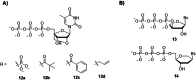
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

