A very complicated UTI: malakoplakia following E. coli urinary tract infection
- PMID: 38890600
- PMCID: PMC11186150
- DOI: 10.1186/s12882-024-03640-9
A very complicated UTI: malakoplakia following E. coli urinary tract infection
Abstract
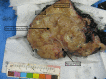
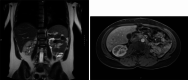
Malakoplakia is a rare inflammatory disorder believed to result from a defect in macrophage phagocytic function triggering a granulomatous reaction. It can present with genitourinary, gastrointestinal, or cutaneous manifestations in immunocompromised or, less commonly, immunocompetent hosts. We describe a case of renal malakoplakia in a young, otherwise healthy patient presenting with nephromegaly and sepsis following an E. coli urinary tract infection. We discuss diagnosis and management, including antibiotic selection and the decision to pursue nephrectomy. This case highlights the potential for kidney recovery with prolonged antibiotic therapy in conjunction with adjunct immunomodulatory therapies and source control.
Keywords: E. coli UTI; Malakoplakia; Michaelis-gutmann bodies.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
None.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Malakoplakia presenting with urinary tract infection, acute kidney injury, and bilateral renal enlargement in an immunocompetent patient.J Nephrol. 2023 Dec;36(9):2641-2643. doi: 10.1007/s40620-023-01796-5. Epub 2023 Nov 4. J Nephrol. 2023. PMID: 37924475 No abstract available.
-
Successful treatment of malakoplakia of the bladder in a kitten.J Feline Med Surg. 2013 Aug;15(8):744-8. doi: 10.1177/1098612X12471663. Epub 2013 Jan 8. J Feline Med Surg. 2013. PMID: 23300187 Free PMC article.
-
Cutaneous malakoplakia.Arch Pathol Lab Med. 2008 Jan;132(1):113-7. doi: 10.5858/2008-132-113-CM. Arch Pathol Lab Med. 2008. PMID: 18181662 Review.
-
Malacoplakia in a renal transplant. Report of a case studied by light and electron microscopy.Scand J Urol Nephrol. 1977;11(1):93-6. doi: 10.3109/00365597709179700. Scand J Urol Nephrol. 1977. PMID: 322266
-
Renal parenchymal malakoplakia--a case report and review of the literature.Pediatr Nephrol. 1993 Jun;7(3):256-8. doi: 10.1007/BF00853212. Pediatr Nephrol. 1993. PMID: 8518093 Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

