The necessity of suction drainage when intra-articular injection of tranexamic acid is used during primary total knee arthroplasty: a retrospective study
- PMID: 38890633
- PMCID: PMC11184754
- DOI: 10.1186/s12891-024-07604-w
The necessity of suction drainage when intra-articular injection of tranexamic acid is used during primary total knee arthroplasty: a retrospective study
Abstract
Background: Suction drainages are commonly used after total knee arthroplasty (TKA) procedures; however, their use is somewhat controversial. Recently, some reports have claimed that the administration of tranexamic acid (TXA) may prevent postoperative bleeding following TKAs. Although numerous studies have reported regarding different dosages, timings of administration, or drain clamping times for intravenous and intra-articular TXA injections (IA-TXAs), few have examined whether suction drainage is necessary when TXA is administered. In this study, we compared using suction drainage without TXA administration and IA-TXA without suction drainage and aimed to examine the need for suction drainage during IA-TXA.
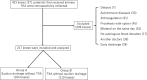
Methods: This retrospective study was conducted on 217 patients who had received TKA for osteoarthritis; 104 were placed on suction drainage after TKA without TXA (Group A), whereas the remaining 113 received IA-TXA immediately after surgery without suction drainage (Group B). Our clinical evaluation included assessments of the need for transfusion, presence of postoperative complications, incidence of deep vein thrombosis (DVT), and changes in hemoglobin (Hb), hematocrit (Hct), and D-dimer levels.
Results: No significant differences were observed in terms of postoperative complications and preoperative Hb, Hct, or D-dimer levels between the two groups. Although the prevalence of DVT was significantly higher in Group B (p < 0.05), all cases were asymptomatic. Hb and Hct levels were significantly lower in Group A than in Group B at 1, 3, 7, and 14 days postoperatively (p < 0.05), although none of the cases required blood transfusions. D-dimer levels were significantly higher in Group A than in Group B at 1 and 3 days postoperatively (p < 0.05).
Conclusion: Suction drainage might not be necessary when IA-TXA is administered after TKA procedures.
Keywords: Intra-articular injection; Suction drainage; Total knee arthroplasty; Tranexamic acid.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical