Comprehensive network of stress-induced responses in Zymomonas mobilis during bioethanol production: from physiological and molecular responses to the effects of system metabolic engineering
- PMID: 38890644
- PMCID: PMC11186258
- DOI: 10.1186/s12934-024-02459-1
Comprehensive network of stress-induced responses in Zymomonas mobilis during bioethanol production: from physiological and molecular responses to the effects of system metabolic engineering
Abstract
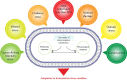
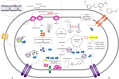
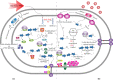
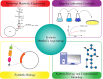
Nowadays, biofuels, especially bioethanol, are becoming increasingly popular as an alternative to fossil fuels. Zymomonas mobilis is a desirable species for bioethanol production due to its unique characteristics, such as low biomass production and high-rate glucose metabolism. However, several factors can interfere with the fermentation process and hinder microbial activity, including lignocellulosic hydrolysate inhibitors, high temperatures, an osmotic environment, and high ethanol concentration. Overcoming these limitations is critical for effective bioethanol production. In this review, the stress response mechanisms of Z. mobilis are discussed in comparison to other ethanol-producing microbes. The mechanism of stress response is divided into physiological (changes in growth, metabolism, intracellular components, and cell membrane structures) and molecular (up and down-regulation of specific genes and elements of the regulatory system and their role in expression of specific proteins and control of metabolic fluxes) changes. Systemic metabolic engineering approaches, such as gene manipulation, overexpression, and silencing, are successful methods for building new metabolic pathways. Therefore, this review discusses systems metabolic engineering in conjunction with systems biology and synthetic biology as an important method for developing new strains with an effective response mechanism to fermentation stresses during bioethanol production. Overall, understanding the stress response mechanisms of Z. mobilis can lead to more efficient and effective bioethanol production.
Keywords: Zymomonas mobilis; Bioethanol fermentation stress condition; Metabolic engineering; Stress response regulatory network; Synthetic biology; Systems biology.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures

References
-
- Ajit A, Sulaiman AZ, Chisti Y. Production of bioethanol by Zymomonas mobilis in high-gravity extractive fermentations. Food Bioprod Process. 2017;102:123–35. doi: 10.1016/j.fbp.2016.12.006. - DOI
-
- Khambhaty Y, Upadhyay D, Kriplani Y, Joshi N, Mody K, Gandhi MR. Bioethanol from Macroalgal Biomass: utilization of Marine yeast for production of the same. Bioenergy Res. 2013;6:188–95. doi: 10.1007/s12155-012-9249-4. - DOI
-
- Hu N, Yuan B, Sun J, Wang S-A, Li F-L. Thermotolerant Kluyveromyces marxianus and Saccharomyces cerevisiae strains representing potentials for bioethanol production from Jerusalem artichoke by consolidated bioprocessing. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2012;95:1359–68. doi: 10.1007/s00253-012-4240-8. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

