Rituximab in the treatment of progressive interstitial lung disease associated with the antisynthetase syndrome
- PMID: 38890654
- PMCID: PMC11184916
- DOI: 10.1186/s13075-024-03353-2
Rituximab in the treatment of progressive interstitial lung disease associated with the antisynthetase syndrome
Erratum in
-
Correction: Rituximab in the treatment of progressive interstitial lung disease associated with the antisynthetase syndrome.Arthritis Res Ther. 2024 Jul 9;26(1):128. doi: 10.1186/s13075-024-03357-y. Arthritis Res Ther. 2024. PMID: 38982531 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
Objective: To assess the real-world, long-term effectiveness of rituximab (RTX) as a rescue therapy in patients with antisynthetase syndrome and progressive interstitial lung disease (ASS-ILD).
Methods: Multicentre observational retrospective longitudinal study of a cohort of patients with ASS-ILD that started treatment with RTX due to recurrent or ongoing progressive ILD despite therapy with glucocorticoids and immunosuppressants.
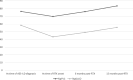
Results: Twenty-eight patients were analyzed. Examining the entire study population, before treatment with RTX the mean decline in %pFVC and %pDLCO from the ASS-ILD diagnosis to the initiation of RTX treatment (T0) was -6.44% and -14.85%, respectively. After six months of treatment, RTX reversed the decline in pulmonary function test (PFT) parameters: ∆%pFVC +6.29% (95% CI: -10.07 to 2.51; p=0.002 compared to T0) and ∆%pDLCO +6.15% (95% CI: -10.86 to -1.43; p=0.013). Twenty-four patients completed one year of therapy and 22 two years, maintaining the response in PFT: ∆%pFVC: +9.93% (95% CI: -15.61 to -4.25; p=0.002) and ∆%pDLCO: +7.66% (95% CI: -11.67 to -3.65; p<0.001). In addition, there was a significant reduction in the median dose of prednisone, and it could be suspended in 18% of cases. In 33% of patients who required oxygen therapy at the start of treatment, it could be discontinued. The frequency of adverse events reached 28.5% of cases.
Conclusion: Based on our results, RTX appears to be effective as rescue therapy in most patients with recurrent or progressive ASS-ILD unresponsive to conventional treatment. The use of RTX was well tolerated in the majority of patients.
Keywords: Antisynthetase syndrome; Progressive interstitial lung disease; Treatment; Rituximab.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- Opinc AH, Makowska JS. Antisynthetase syndrome - much more than just a myopathy. Semin Arthritis Rheum. 2021;51:72–83. - PubMed
-
- Marco JL, Collins BF. Clinical manifestations and treatment of antisynthetase síndrome. Best Pract Res Clin Rheumatol. 2020;34:101503. - PubMed
-
- Wang R, Zhao Y, Qi F, Wu X, Wang Y, Xu Y, et al. Analysis of the clinical features of antisynthetase syndrome: a retrospective cohort study in China. Clin Rheumatol. 2023;42:703–709. - PubMed
-
- Gasparotto M, Gatto M, Saccon F, Ghirardello A, Iaccarino L, Doria A. Pulmonary involvement in antisynthetase syndrome. Curr Opin Rheumatol. 2019;31:603–610. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Supplementary concepts
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous