Noninvasive prediction of lymph node metastasis in pancreatic cancer using an ultrasound-based clinicoradiomics machine learning model
- PMID: 38890695
- PMCID: PMC11184715
- DOI: 10.1186/s12938-024-01259-3
Noninvasive prediction of lymph node metastasis in pancreatic cancer using an ultrasound-based clinicoradiomics machine learning model
Abstract
Objectives: This study was designed to explore and validate the value of different machine learning models based on ultrasound image-omics features in the preoperative diagnosis of lymph node metastasis in pancreatic cancer (PC).
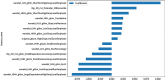
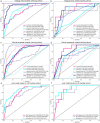
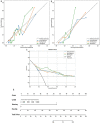
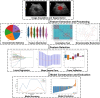
Methods: This research involved 189 individuals diagnosed with PC confirmed by surgical pathology (training cohort: n = 151; test cohort: n = 38), including 50 cases of lymph node metastasis. Image-omics features were extracted from ultrasound images. After dimensionality reduction and screening, eight machine learning algorithms, including logistic regression (LR), support vector machine (SVM), K-nearest neighbors (KNN), random forest (RF), extra trees (ET), extreme gradient boosting (XGBoost), light gradient boosting machine (LightGBM), and multilayer perceptron (MLP), were used to establish image-omics models to predict lymph node metastasis in PC. The best omics prediction model was selected through ROC curve analysis. Machine learning models were used to analyze clinical features and determine variables to establish a clinical model. A combined model was constructed by combining ultrasound image-omics and clinical features. Decision curve analysis (DCA) and a nomogram were used to evaluate the clinical application value of the model.
Results: A total of 1561 image-omics features were extracted from ultrasound images. 15 valuable image-omics features were determined by regularization, dimension reduction, and algorithm selection. In the image-omics model, the LR model showed higher prediction efficiency and robustness, with an area under the ROC curve (AUC) of 0.773 in the training set and an AUC of 0.850 in the test set. The clinical model constructed by the boundary of lesions in ultrasound images and the clinical feature CA199 (AUC = 0.875). The combined model had the best prediction performance, with an AUC of 0.872 in the training set and 0.918 in the test set. The combined model showed better clinical benefit according to DCA, and the nomogram score provided clinical prediction solutions.
Conclusion: The combined model established with clinical features has good diagnostic ability and can be used to predict lymph node metastasis in patients with PC. It is expected to provide an effective noninvasive method for clinical decision-making, thereby improving the diagnosis and treatment of PC.
Keywords: Lymph node metastasis; Machine learning; Pancreatic cancer; Radiomics; Ultrasound.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Prediction of lateral lymph node metastasis with short diameter less than 8 mm in papillary thyroid carcinoma based on radiomics.Cancer Imaging. 2024 Nov 15;24(1):155. doi: 10.1186/s40644-024-00803-7. Cancer Imaging. 2024. PMID: 39548590 Free PMC article.
-
[Clinical study of cervical lymph node metastasis in oral tongue squamous carcinoma by a machine learning model based on contrast-enhanced CT radiomics].Shanghai Kou Qiang Yi Xue. 2024 Dec;33(6):608-616. Shanghai Kou Qiang Yi Xue. 2024. PMID: 40007291 Chinese.
-
Machine Learning Model for Predicting Axillary Lymph Node Metastasis in Clinically Node Positive Breast Cancer Based on Peritumoral Ultrasound Radiomics and SHAP Feature Analysis.J Ultrasound Med. 2024 Sep;43(9):1611-1625. doi: 10.1002/jum.16483. Epub 2024 May 29. J Ultrasound Med. 2024. PMID: 38808580
-
The CMLA score: A novel tool for early prediction of renal replacement therapy in patients with cardiogenic shock.Curr Probl Cardiol. 2024 Dec;49(12):102870. doi: 10.1016/j.cpcardiol.2024.102870. Epub 2024 Sep 27. Curr Probl Cardiol. 2024. PMID: 39343053 Review.
-
A systematic review on machine learning approaches in cerebral palsy research.PeerJ. 2024 Oct 18;12:e18270. doi: 10.7717/peerj.18270. eCollection 2024. PeerJ. 2024. PMID: 39434788 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Accuracy of dual-contrast gastrointestinal ultrasonography in predicting lymph node metastasis in older adults with gastric cancer.World J Gastrointest Oncol. 2025 May 15;17(5):104194. doi: 10.4251/wjgo.v17.i5.104194. World J Gastrointest Oncol. 2025. PMID: 40487969 Free PMC article.
-
Preoperative prediction of lymph node metastasis in intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma: an integrative approach combining ultrasound-based radiomics and inflammation-related markers.BMC Med Imaging. 2025 Jan 2;25(1):4. doi: 10.1186/s12880-024-01542-8. BMC Med Imaging. 2025. PMID: 39748308 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Pandya G, Kirtonia A, Singh A, Goel A, Mohan CD, Rangappa KS, Pandey AK, Kapoor S, Tandon S, Sethi G, Garg M. A comprehensive review of the multifaceted role of the microbiota in human pancreatic carcinoma. Semin Cancer Biol. 2022;86(Pt 3):682–692. doi: 10.1016/j.semcancer.2021.05.027. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

