The relationship between the psychological resilience and post-traumatic growth of college students during the COVID-19 pandemic: a model of conditioned processes mediated by negative emotions and moderated by deliberate rumination
- PMID: 38890704
- PMCID: PMC11186135
- DOI: 10.1186/s40359-024-01853-z
The relationship between the psychological resilience and post-traumatic growth of college students during the COVID-19 pandemic: a model of conditioned processes mediated by negative emotions and moderated by deliberate rumination
Abstract
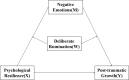
Background: The mental health of university students during the COVID-19 pandemic has attracted the attention of researchers. For the present study researchers constructed a mediation model to explore the relationship between psychological resilience and post-traumatic growth, the mediating role of negative emotions and the moderating role of deliberate rumination in students.
Methods: The Psychological Resilience Scale, Posttraumatic Growth Inventory, Depression-Anxiety-Stress Scale (DASS-21) and Event Related Rumination Inventory were used in a survey of 881 college students. The data were analyzed using SPSS 26.0 and the PROCESS plugin (version 3.3).
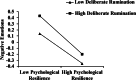
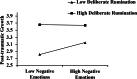
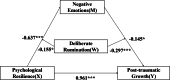
Results: (1) Psychological resilience is positively related with post-traumatic growth. Deliberate rumination is positively related to psychological resilience, posttraumatic growth, and negative emotions. Psychological resilience, post-traumatic growth and negative emotions are negatively related. (2) Negative emotions mediated the relationship between psychological resilience and post-traumatic growth. (3) Deliberate rumination plays a moderating role in psychological resilience affecting negative emotions. Deliberate rumination plays a moderating role in the extent to which psychological resilience influences PTG through negative emotions.
Conclusions: Psychological resilience affects post-traumatic growth directly and also indirectly through negative emotions. With the increase of mental resilience, the level of negative emotion tended to decrease. When individuals are experiencing negative emotions, high levels of active rumination are more likely to promote post-traumatic growth. This study helps to explore the factors affecting the mental health of college students during the epidemic, thus providing guidance for appropriate mental health interventions.
Keywords: COVID-19; Deliberate rumination; Moderated mediation model; Negative emotions; Post-traumatic growth; Psychological resilience.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The Impact of Intrusive Rumination on College Students' Creativity During the COVID-19 Pandemic: The Mediating Effect of Post-traumatic Growth and the Moderating Role of Psychological Resilience.Front Psychol. 2022 Apr 11;13:789844. doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2022.789844. eCollection 2022. Front Psychol. 2022. PMID: 35478749 Free PMC article.
-
The Influence of Post-Traumatic Growth on College Students' Creativity During the COVID-19 Pandemic: The Mediating Role of General Self-Efficacy and the Moderating Role of Deliberate Rumination.Front Psychol. 2021 Apr 14;12:665973. doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2021.665973. eCollection 2021. Front Psychol. 2021. PMID: 33935927 Free PMC article.
-
The influence of deliberate rumination on the post-traumatic growth of college students during the COVID-19 pandemic and the moderating role of self-efficacy.Front Public Health. 2023 Feb 2;11:1043402. doi: 10.3389/fpubh.2023.1043402. eCollection 2023. Front Public Health. 2023. PMID: 36817884 Free PMC article.
-
A meta-analysis of the association between event-related rumination and posttraumatic growth: The Event-Related Rumination Inventory and the Posttraumatic Growth Inventory.J Trauma Stress. 2022 Dec;35(6):1575-1585. doi: 10.1002/jts.22875. Epub 2022 Sep 5. J Trauma Stress. 2022. PMID: 36065484 Review.
-
[A Structural Equation Model for Posttraumatic Growth among Cured Patients with COVID-19].J Korean Acad Nurs. 2023 Jun;53(3):309-323. doi: 10.4040/jkan.22118. J Korean Acad Nurs. 2023. PMID: 37435762 Review. Korean.
Cited by
-
Post-Traumatic Growth in Volunteers Following the 2023 Kahramanmaraş Earthquakes.Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2025 Apr 28;22(5):699. doi: 10.3390/ijerph22050699. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2025. PMID: 40427816 Free PMC article.
-
Supervisor-postgraduate relationship and perceived stress: the mediating role of self-efficacy and the moderating role of psychological resilience.BMC Psychol. 2024 Dec 20;12(1):769. doi: 10.1186/s40359-024-02251-1. BMC Psychol. 2024. PMID: 39707497 Free PMC article.
-
Investigating the Impact of a Psychoeducational Program on Self-Disclosure, Posttraumatic Growth and Resilience for Adolescents.J Child Adolesc Trauma. 2025 Feb 19;18(2):365-375. doi: 10.1007/s40653-025-00694-1. eCollection 2025 Jun. J Child Adolesc Trauma. 2025. PMID: 40469796
-
The current state and influencing factors of negative social expectations among thyroid cancer patients: a single-center cross-sectional analysis.Front Psychol. 2025 May 12;16:1599652. doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2025.1599652. eCollection 2025. Front Psychol. 2025. PMID: 40420988 Free PMC article.
-
Mobile phone addiction and negative emotions: an empirical study among adolescents in Jiangxi Province.Front Psychiatry. 2025 Jan 27;16:1541605. doi: 10.3389/fpsyt.2025.1541605. eCollection 2025. Front Psychiatry. 2025. PMID: 39931699 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

