CT-based delta-radiomics nomogram to predict pathological complete response after neoadjuvant chemoradiotherapy in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma patients
- PMID: 38890720
- PMCID: PMC11186275
- DOI: 10.1186/s12967-024-05392-4
CT-based delta-radiomics nomogram to predict pathological complete response after neoadjuvant chemoradiotherapy in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma patients
Abstract
Background: This study developed a nomogram model using CT-based delta-radiomics features and clinical factors to predict pathological complete response (pCR) in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma (ESCC) patients receiving neoadjuvant chemoradiotherapy (nCRT).
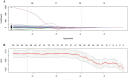
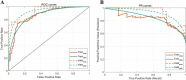
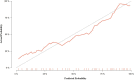
Methods: The study retrospectively analyzed 232 ESCC patients who underwent pretreatment and post-treatment CT scans. Patients were divided into training (n = 186) and validation (n = 46) sets through fivefold cross-validation. 837 radiomics features were extracted from regions of interest (ROIs) delineations on CT images before and after nCRT to calculate delta values. The LASSO algorithm selected delta-radiomics features (DRF) based on classification performance. Logistic regression constructed a nomogram incorporating DRFs and clinical factors. Receiver operating characteristic (ROC) and area under the curve (AUC) analyses evaluated nomogram performance for predicting pCR.
Results: No significant differences existed between the training and validation datasets. The 4-feature delta-radiomics signature (DRS) demonstrated good predictive accuracy for pCR, with α-binormal-based and empirical AUCs of 0.871 and 0.869. T-stage (p = 0.001) and differentiation degree (p = 0.018) were independent predictors of pCR. The nomogram combined the DRS and clinical factors improved the classification performance in the training dataset (AUCαbin = 0.933 and AUCemp = 0.941). The validation set showed similar performance with AUCs of 0.958 and 0.962.
Conclusions: The CT-based delta-radiomics nomogram model with clinical factors provided high predictive accuracy for pCR in ESCC patients after nCRT.
Keywords: Computed tomography; Delta-radiomics; Esophageal squamous cell carcinoma; Neoadjuvant chemoradiotherapy; Pathological complete response.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures



Similar articles
-
A nomogram based on pretreatment CT radiomics features for predicting complete response to chemoradiotherapy in patients with esophageal squamous cell cancer.Radiat Oncol. 2020 Oct 29;15(1):249. doi: 10.1186/s13014-020-01692-3. Radiat Oncol. 2020. PMID: 33121507 Free PMC article.
-
Predicting anastomotic leak in patients with esophageal squamous cell cancer treated with neoadjuvant chemoradiotherapy using a nomogram based on CT radiomic and clinicopathologic factors.BMC Cancer. 2025 Mar 15;25(1):484. doi: 10.1186/s12885-025-13884-9. BMC Cancer. 2025. PMID: 40089723 Free PMC article.
-
Development of a nomogram for the prediction of pathological complete response after neoadjuvant chemoradiotherapy in patients with esophageal squamous cell carcinoma.Dis Esophagus. 2017 Feb 1;30(2):1-8. doi: 10.1111/dote.12519. Dis Esophagus. 2017. PMID: 27868287
-
CT radiomics to predict pathologic complete response after neoadjuvant immunotherapy plus chemoradiotherapy in locally advanced esophageal squamous cell carcinoma.Eur Radiol. 2025 Mar;35(3):1594-1604. doi: 10.1007/s00330-024-11141-4. Epub 2024 Oct 29. Eur Radiol. 2025. PMID: 39470794
-
Development and validation a radiomics combined clinical model predicts treatment response for esophageal squamous cell carcinoma patients.BMC Gastroenterol. 2025 Apr 29;25(1):313. doi: 10.1186/s12876-025-03899-8. BMC Gastroenterol. 2025. PMID: 40301780 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
CT delta-radiomics predicts the risks of blood transfusion and massive bleeding during spinal tumor surgery.Cancer Imaging. 2025 Jun 22;25(1):79. doi: 10.1186/s40644-025-00900-1. Cancer Imaging. 2025. PMID: 40545537 Free PMC article.
-
Deep learning radiomics for the prediction of epidermal growth factor receptor mutation status based on MRI in brain metastasis from lung adenocarcinoma patients.BMC Cancer. 2025 Mar 12;25(1):443. doi: 10.1186/s12885-025-13823-8. BMC Cancer. 2025. PMID: 40075375 Free PMC article.
-
A comprehensive nomogram for assessing the prognosis of non-small cell lung cancer patients receiving immunotherapy: a prospective cohort study in China.Front Immunol. 2024 Nov 20;15:1487078. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1487078. eCollection 2024. Front Immunol. 2024. PMID: 39635526 Free PMC article.
-
The diagnostic value of a nomogram based on enhanced CT radiomics for differentiating between intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma and early hepatic abscess.Front Mol Biosci. 2024 Aug 23;11:1409060. doi: 10.3389/fmolb.2024.1409060. eCollection 2024. Front Mol Biosci. 2024. PMID: 39247207 Free PMC article.
-
Predicting the immune therapy response of advanced non-small cell lung cancer based on primary tumor and lymph node radiomics features.Front Med (Lausanne). 2025 Apr 3;12:1541376. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2025.1541376. eCollection 2025. Front Med (Lausanne). 2025. PMID: 40248083 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Shapiro J, Van Lanschot JJB, Hulshof MC, van Hagen P, van Berge Henegouwen MI, Wijnhoven BP, et al. Neoadjuvant chemoradiotherapy plus surgery versus surgery alone for oesophageal or junctional cancer (CROSS): long-term results of a randomised controlled trial. Lancet Oncol. 2015;16(9):1090–1098. doi: 10.1016/S1470-2045(15)00040-6. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
- flzh202123/Radiation Oncology Translational Medicine Foundation for Scientific Research of Bethune
- YXH2022ZX02196/Shandong Medical Association Clinical Research Fund
- 20220511/Jinan Science and Technology Clinical Medicine Innovation Plan
- 20238073/Jinan Science and Technology Clinical Medicine Innovation Plan
- SDYWZGKCJH2022018/Shandong Provincial Medical System Staff Science and Technology Innovation Program
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

