Advances in nanomaterial-targeted treatment of acute lung injury after burns
- PMID: 38890721
- PMCID: PMC11184898
- DOI: 10.1186/s12951-024-02615-0
Advances in nanomaterial-targeted treatment of acute lung injury after burns
Abstract
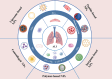
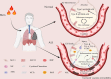
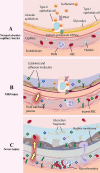
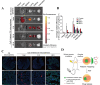
Acute lung injury (ALI) is a common complication in patients with severe burns and has a complex pathogenesis and high morbidity and mortality rates. A variety of drugs have been identified in the clinic for the treatment of ALI, but they have toxic side effects caused by easy degradation in the body and distribution throughout the body. In recent years, as the understanding of the mechanism underlying ALI has improved, scholars have developed a variety of new nanomaterials that can be safely and effectively targeted for the treatment of ALI. Most of these methods involve nanomaterials such as lipids, organic polymers, peptides, extracellular vesicles or cell membranes, inorganic nanoparticles and other nanomaterials, which are targeted to reach lung tissues to perform their functions through active targeting or passive targeting, a process that involves a variety of cells or organelles. In this review, first, the mechanisms and pathophysiological features of ALI occurrence after burn injury are reviewed, potential therapeutic targets for ALI are summarized, existing nanomaterials for the targeted treatment of ALI are classified, and possible problems and challenges of nanomaterials in the targeted treatment of ALI are discussed to provide a reference for the development of nanomaterials for the targeted treatment of ALI.
Keywords: ALI; Burn; Camouflaged nanoparticles; Nanomaterials; Targeted treatment.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Exosomes of different cellular origins: prospects and challenges in the treatment of acute lung injury after burns.J Mater Chem B. 2025 Jan 29;13(5):1531-1547. doi: 10.1039/d4tb02351j. J Mater Chem B. 2025. PMID: 39704476 Review.
-
Cell-derived biomimetic nanoparticles for the targeted therapy of ALI/ARDS.Drug Deliv Transl Res. 2024 Jun;14(6):1432-1457. doi: 10.1007/s13346-023-01494-6. Epub 2023 Dec 20. Drug Deliv Transl Res. 2024. PMID: 38117405 Review.
-
Targeting delivery of simvastatin using ICAM-1 antibody-conjugated nanostructured lipid carriers for acute lung injury therapy.Drug Deliv. 2017 Nov;24(1):402-413. doi: 10.1080/10717544.2016.1259369. Drug Deliv. 2017. PMID: 28165814 Free PMC article.
-
Novel application of nanomedicine for the treatment of acute lung injury: a literature review.Ther Adv Respir Dis. 2024 Jan-Dec;18:17534666241244974. doi: 10.1177/17534666241244974. Ther Adv Respir Dis. 2024. PMID: 38616385 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Engineering of targeting antioxidant polypeptide nanopolyplexes for the treatment of acute lung injury.Int J Biol Macromol. 2024 Jan;254(Pt 3):127872. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2023.127872. Epub 2023 Nov 7. Int J Biol Macromol. 2024. PMID: 37939759
Cited by
-
Curcumin-loaded nanoemulsion for acute lung injury treatment via nebulization: Formulation, optimization and in vivo studies.ADMET DMPK. 2025 Mar 20;13(2):2661. doi: 10.5599/admet.2661. eCollection 2025. ADMET DMPK. 2025. PMID: 40314003 Free PMC article.
-
[Amentoflavone alleviates acute lung injury in mice by inhibiting cell pyroptosis].Nan Fang Yi Ke Da Xue Xue Bao. 2025 Apr 20;45(4):692-701. doi: 10.12122/j.issn.1673-4254.2025.04.03. Nan Fang Yi Ke Da Xue Xue Bao. 2025. PMID: 40294918 Free PMC article. Chinese.
-
Selenium nanoparticles activate selenoproteins to mitigate septic lung injury through miR-20b-mediated RORγt/STAT3/Th17 axis inhibition and enhanced mitochondrial transfer in BMSCs.J Nanobiotechnology. 2025 Mar 20;23(1):226. doi: 10.1186/s12951-025-03312-2. J Nanobiotechnology. 2025. PMID: 40114196 Free PMC article.
-
Extracellular vesicles from adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells alleviate acute lung injury via the CBL/AMPK signaling pathway.BMC Biol. 2025 Mar 31;23(1):90. doi: 10.1186/s12915-025-02178-y. BMC Biol. 2025. PMID: 40165177 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
- 52202343, 82172204/National Natural Science Foundation of China
- 2022zhyx-C01/the Research Fund of Anhui Institute of Translational Medicine
- 2021xkT028/the Basic and Clinical Cooperative Research and Promotion Program of Anhui Medical University
- 202104j07020027/the Anhui Key Research and Development Plan
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

