Exosomes as drug delivery systems in glioma immunotherapy
- PMID: 38890722
- PMCID: PMC11184820
- DOI: 10.1186/s12951-024-02611-4
Exosomes as drug delivery systems in glioma immunotherapy
Abstract
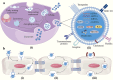
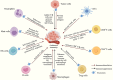
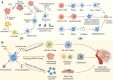
Recently, the significant benefits of cancer immunotherapy for most cancers have been demonstrated in clinical and preclinical studies. However, the efficacy of these immunotherapies for gliomas is limited, owing to restricted drug delivery and insufficient immune activation. As drug carriers, exosomes offer the advantages of low toxicity, good biocompatibility, and intrinsic cell targeting, which could enhance glioma immunotherapy efficacy. However, a review of exosome-based drug delivery systems for glioma immunotherapy has not been presented. This review introduces the current problems in glioma immunotherapy and the role of exosomes in addressing these issues. Meanwhile, preparation and application strategies of exosome-based drug delivery systems for glioma immunotherapy are discussed, especially for enhancing immunogenicity and reversing the immunosuppressive tumor microenvironment. Finally, we briefly describe the challenges of exosome-based drug delivery systems in clinical translation. We anticipate that this review will guide the use of exosomes as drug carriers for glioma immunotherapy.
Keywords: Drug delivery systems; Exosomes; Glioma; Immunotherapy.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

