Targeting SUMOylation with an injectable nanocomposite hydrogel to optimize radiofrequency ablation therapy for hepatocellular carcinoma
- PMID: 38890737
- PMCID: PMC11184877
- DOI: 10.1186/s12951-024-02579-1
Targeting SUMOylation with an injectable nanocomposite hydrogel to optimize radiofrequency ablation therapy for hepatocellular carcinoma
Erratum in
-
Correction:Targeting SUMOylation with an injectable nanocomposite hydrogel to optimize radiofrequency ablation therapy for hepatocellular carcinoma.J Nanobiotechnology. 2024 Aug 2;22(1):462. doi: 10.1186/s12951-024-02690-3. J Nanobiotechnology. 2024. PMID: 39095907 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
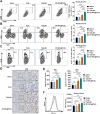
Background: Incomplete radiofrequency ablation (iRFA) in hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) often leads to local recurrence and distant metastasis of the residual tumor. This is closely linked to the development of a tumor immunosuppressive environment (TIME). In this study, underlying mechanisms and potential therapeutic targets involved in the formation of TIME in residual tumors following iRFA were explored. Then, TAK-981-loaded nanocomposite hydrogel was constructed, and its therapeutic effects on residual tumors were investigated.
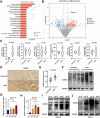
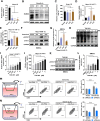
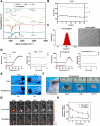
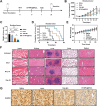
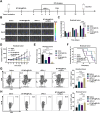
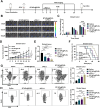
Results: This study reveals that the upregulation of small ubiquitin-like modifier 2 (Sumo2) and activated SUMOylation is intricately tied to immunosuppression in residual tumors post-iRFA. Both knockdown of Sumo2 and inhibiting SUMOylation with TAK-981 activate IFN-1 signaling in HCC cells, thereby promoting dendritic cell maturation. Herein, we propose an injectable PDLLA-PEG-PDLLA (PLEL) nanocomposite hydrogel which incorporates self-assembled TAK-981 and BSA nanoparticles for complementary localized treatment of residual tumor after iRFA. The sustained release of TAK-981 from this hydrogel curbs the expansion of residual tumors and notably stimulates the dendritic cell and cytotoxic lymphocyte-mediated antitumor immune response in residual tumors while maintaining biosafety. Furthermore, the treatment with TAK-981 nanocomposite hydrogel resulted in a widespread elevation in PD-L1 levels. Combining TAK-981 nanocomposite hydrogel with PD-L1 blockade therapy synergistically eradicates residual tumors and suppresses distant tumors.
Conclusions: These findings underscore the potential of the TAK-981-based strategy as an effective therapy to enhance RFA therapy for HCC.
Keywords: Hepatocellular carcinoma; Nanocomposite hydrogel; Radiofrequency ablation; Small ubiquitin-like modifier 2; TAK-981.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that no conflict of interest exists.
Figures
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

