Unveiling the Chemistry of Citrus Peel: Insights into Nutraceutical Potential and Therapeutic Applications
- PMID: 38890908
- PMCID: PMC11172398
- DOI: 10.3390/foods13111681
Unveiling the Chemistry of Citrus Peel: Insights into Nutraceutical Potential and Therapeutic Applications
Abstract
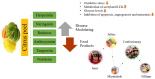
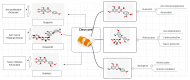
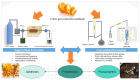
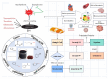
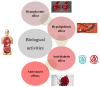
The recent millennium has witnessed a notable shift in consumer focus towards natural products for addressing lifestyle-related disorders, driven by their safety and cost-effectiveness. Nutraceuticals and functional foods play an imperative role by meeting nutritional needs and offering medicinal benefits. With increased scientific knowledge and awareness, the significance of a healthy lifestyle, including diet, in reducing disease risk is widely acknowledged, facilitating access to a diverse and safer diet for longevity. Plant-based foods rich in phytochemicals are increasingly popular and effectively utilized in disease management. Agricultural waste from plant-based foods is being recognized as a valuable source of nutraceuticals for dietary interventions. Citrus peels, known for their diverse flavonoids, are emerging as a promising health-promoting ingredient. Globally, citrus production yields approximately 15 million tons of by-products annually, highlighting the substantial potential for utilizing citrus waste in phyto-therapeutic and nutraceutical applications. Citrus peels are a rich source of flavonoids, with concentrations ranging from 2.5 to 5.5 g/100 g dry weight, depending on the citrus variety. The most abundant flavonoids in citrus peel include hesperidin and naringin, as well as essential oils rich in monoterpenes like limonene. The peel extracts exhibit high antioxidant capacity, with DPPH radical scavenging activities ranging from 70 to 90%, comparable to synthetic antioxidants like BHA and BHT. Additionally, the flavonoids present in citrus peel have been found to have antioxidant properties, which can help reduce oxidative stress by 30% and cardiovascular disease by 25%. Potent anti-inflammatory effects have also been demonstrated, reducing inflammatory markers such as IL-6 and TNF-α by up to 40% in cell culture studies. These findings highlight the potential of citrus peel as a valuable source of nutraceuticals in diet-based therapies.
Keywords: antidiabetic; citrus peel; extraction; hyperlipidemia; hypoglycemic; supercritical.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Galasso C., Gentile A., Orefice I., Ianora A., Bruno A., Noonan D.M., Sansone C., Albini A., Brunet C. Microalgal derivatives as potential nutraceutical and food supplements for human health: A focus on cancer prevention and interception. Nutrients. 2019;11:1226. doi: 10.3390/nu11061226. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Awan K.A., Butt M.S., Munir H., Suleria H.A.R. Bioactive Compounds from Plant Origin. Apple Academic Press; Waretown, NJ, USA: 2019. Garlic: From nutritional to nutraceutical viewpoint; pp. 235–266.
-
- AlAli M., Alqubaisy M., Aljaafari M.N., AlAli A.O., Baqais L., Molouki A., Abushelaibi A., Lai K.-S., Lim S.-H.E. Nutraceuticals: Transformation of conventional foods into health promoters/disease preventers and safety considerations. Molecules. 2021;26:2540. doi: 10.3390/molecules26092540. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Wang J., Zhao H., Wang Y., Lau H., Zhou W., Chen C., Tan S. A review of stevia as a potential healthcare product: Up-to-date functional characteristics, administrative standards and engineering techniques. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2020;103:264–281. doi: 10.1016/j.tifs.2020.07.023. - DOI
-
- Gulati O.P., Ottaway P.B., Jennings S., Coppens P., Gulati N. Nutraceutical and Functional Food Regulations in the United States and around the World. Elsevier; Amsterdam, The Netherlands: 2019. Botanical nutraceuticals (food supplements and fortified and functional foods) and novel foods in the EU, with a main focus on legislative controls on safety aspects; pp. 277–321.
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

