Biosynthesis and Biotechnological Synthesis of Hydroxytyrosol
- PMID: 38890922
- PMCID: PMC11171820
- DOI: 10.3390/foods13111694
Biosynthesis and Biotechnological Synthesis of Hydroxytyrosol
Abstract
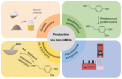
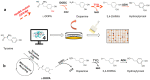
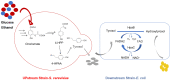
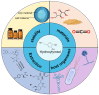
Hydroxytyrosol (HT), a plant-derived phenolic compound, is recognized for its potent antioxidant capabilities alongside a spectrum of pharmacological benefits, including anti-inflammatory, anti-cancer, anti-bacterial, and anti-viral properties. These attributes have propelled HT into the spotlight as a premier nutraceutical and food additive, heralding a new era in health and wellness applications. Traditional methods for HT production, encompassing physico-chemical techniques and plant extraction, are increasingly being supplanted by biotechnological approaches. These modern methodologies offer several advantages, notably environmental sustainability, safety, and cost-effectiveness, which align with current demands for green and efficient production processes. This review delves into the biosynthetic pathways of HT, highlighting the enzymatic steps involved and the pivotal role of genetic and metabolic engineering in enhancing HT yield. It also surveys the latest progress in the biotechnological synthesis of HT, examining innovative strategies that leverage both genetically modified and non-modified organisms. Furthermore, this review explores the burgeoning potential of HT as a nutraceutical, underscoring its diverse applications and the implications for human health. Through a detailed examination of both the biosynthesis and biotechnological advances in HT production, this review contributes valuable insights to the field, charting a course towards the sustainable and scalable production of this multifaceted compound.
Keywords: industrial applications; nutraceutical; olive leaves; sustainable production; synthetic biology.
Conflict of interest statement
Authors Chenchen Qi and Guohui Chen were employed by the company ACK Co., Ltd. They participated in the methodology, validation, formal analysis, and investigation in this study. The company played no role. The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as potential conflicts of interest.
Figures

References
Publication types
Grants and funding
- 32372298/National Natural Science Foundation of China
- 2022LQ02003/Xinjiang 'Two Zones' Science and Technology Development Plan Project
- 19008022080/Beijing Engineering Technology Research Center Platform Construction Project
- 19008021085/The Construction of High-Precision Disciplines in Beijing-Food Science and Engineering
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

