Online System for Monitoring the Degree of Fermentation of Oolong Tea Using Integrated Visible-Near-Infrared Spectroscopy and Image-Processing Technologies
- PMID: 38890936
- PMCID: PMC11171755
- DOI: 10.3390/foods13111708
Online System for Monitoring the Degree of Fermentation of Oolong Tea Using Integrated Visible-Near-Infrared Spectroscopy and Image-Processing Technologies
Abstract
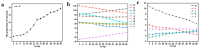
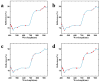
During the fermentation process of Oolong tea, significant changes occur in both its external characteristics and its internal components. This study aims to determine the fermentation degree of Oolong tea using visible-near-infrared spectroscopy (vis-VIS-NIR) and image processing. The preprocessed vis-VIS-NIR spectral data are fused with image features after sequential projection algorithm (SPA) feature selection. Subsequently, traditional machine learning and deep learning classification models are compared, with the support vector machine (SVM) and convolutional neural network (CNN) models yielding the highest prediction rates among traditional machine learning models and deep learning models with 97.14% and 95.15% in the prediction set, respectively. The results indicate that VIS-NIR combined with image processing possesses the capability for rapid non-destructive online determination of the fermentation degree of Oolong tea. Additionally, the predictive rate of traditional machine learning models exceeds that of deep learning models in this study. This study provides a theoretical basis for the fermentation of Oolong tea.
Keywords: Oolong tea; data fusion; fermentation; machine learning; prediction.
Conflict of interest statement
Authors Zhang Han, Yuting Gong, and Chunchi Huang are employed by Chi Chun Machinery (Xiamen) Co., Ltd. Author Zhang Han participated in the investigation. Author Yuting Gong participated in the formal analysis. Author Chunchi Huang participated in the data curation of this study. The company provided materials and equipment but did not provide financial support. The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures




References
-
- Lin Y., Yu W., Zhou L., Fan X., Wang F., Wang P., Fang W., Cai C., Ye N. Genetic diversity of oolong tea (Camellia sinensis) germplasms based on the nanofluidic array of single-nucleotide polymorphism (SNP) markers. Tree Genet. Genomes. 2019;16:3. doi: 10.1007/s11295-019-1392-z. - DOI
-
- Theppakorn T. Stability and chemical changes of phenolic compounds during Oolong tea processing. Int. Food Res. J. 2016;23:564.
-
- Li L., Wang Y., Cui Q., Liu Y., Ning J., Zhang Z. Qualitative and quantitative quality evaluation of black tea fermentation through noncontact chemical imaging. J. Food Compos. Anal. 2022;106:104300. doi: 10.1016/j.jfca.2021.104300. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

