Kidney Bean Protein Prevents High-Fat and High-Fructose Diet-Induced Obesity, Cognitive Impairment, and Disruption of Gut Microbiota Composition
- PMID: 38890944
- PMCID: PMC11171623
- DOI: 10.3390/foods13111718
Kidney Bean Protein Prevents High-Fat and High-Fructose Diet-Induced Obesity, Cognitive Impairment, and Disruption of Gut Microbiota Composition
Abstract
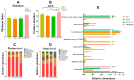
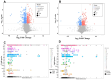
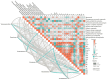
A long-term intake of a high-fat and high-fructose diet (HFFD), even a high-fat, high-fructose but low-protein diet (HFFD + LP), could cause obesity associated with cognitive impairments. In the present study, rats were subjected to a normal diet (ND), an HFFD diet, an HFFD + LP diet, and an HFFD with kidney bean protein (KP) diet for 8 weeks to evaluate the effect of KP on HFFD- or HFFD + LP-induced obesity and cognitive impairment. The results demonstrated that compared with the HFFD diet, KP administration significantly decreased the body weight by 7.7% and the serum Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme 2 (ACE-2) and Insulin-like Growth Factor 1 (IGF-1) levels by 14.4% and 46.8%, respectively (p < 0.05). In addition, KP suppressed HFFD-induced cognitive impairment, which was evidenced by 8.7% less time required to pass the water maze test. The 16s RNA analysis of the colonic contents showed that the relative abundance of Bifidobacterium, Butyricimonas, and Alloprevotella was increased by KP by 5.9, 44.2, and 79.2 times. Additionally, KP supplementation primarily affected the choline metabolic pathway in the liver, and the synthesis and functional pathway of neurotransmitters in the brain, thereby improving obesity and cognitive function in rats.
Keywords: cognitive impairment; gut microbiota; kidney bean protein; obesity.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures



References
-
- Li C., Li W., Yang H., Mi Z., Tan S., Lei X. Polysaccharides from Tumorous stem mustard prevented high fructose diet-induced non-alcoholic fatty liver disease by regulating gut microbiota, hepatic lipid metabolism, and the AKT/FOXO1/MAPK signaling pathway. J. Funct. Foods. 2023;102:105448. doi: 10.1016/j.jff.2023.105448. - DOI
-
- Shi H., Wang Q., Zheng M., Hao S., Lum J.S., Chen X., Huang X.-F., Yu Y., Zheng K. Supplement of microbiota-accessible carbohydrates prevents neuroinflammation and cognitive decline by improving the gut microbiota-brain axis in diet-induced obese mice. J. Neuroinflamm. 2020;17:77. doi: 10.1186/s12974-020-01760-1. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Grants and funding
- 2021YFD1600100/Special National Key Research and Development Plan
- CARS-08-G21/the Key Laboratory of Grain Crop Genetic Resources Evaluation and Utilization, China Agriculture Research System of MOF and MARA
- 01-ICS-02/the Agricultural Science and Technology Innovation Program of the Chinese Academy of Agri-cultural Sciences
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

