(-)-Gallocatechin Gallate Mitigates Metabolic Syndrome-Associated Diabetic Nephropathy in db/db Mice
- PMID: 38890983
- PMCID: PMC11171689
- DOI: 10.3390/foods13111755
(-)-Gallocatechin Gallate Mitigates Metabolic Syndrome-Associated Diabetic Nephropathy in db/db Mice
Abstract
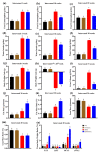
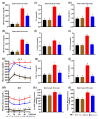
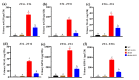
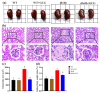
Metabolic syndrome (MetS) significantly predisposes individuals to diabetes and is a prognostic factor for the progression of diabetic nephropathy (DN). This study aimed to evaluate the efficacy of (-)-gallocatechin gallate (GCG) in alleviating signs of MetS-associated DN in db/db mice. We administered GCG and monitored its effects on several metabolic parameters, including food and water intake, urinary output, blood glucose levels, glucose and insulin homeostasis, lipid profiles, blood pressure, and renal function biomarkers. The main findings indicated that GCG intervention led to marked improvements in these metabolic indicators and renal function, signifying its potential in managing MetS and DN. Furthermore, transcriptome analysis revealed substantial modifications in gene expression, notably the downregulation of pro-inflammatory genes such as S100a8, S100a9, Cd44, Socs3, Mmp3, Mmp9, Nlrp3, IL-1β, Osm, Ptgs2, and Lcn2 and the upregulation of the anti-oxidative gene Gstm3. These genetic alterations suggest significant effects on pathways related to inflammation and oxidative stress. In conclusion, GCG demonstrates therapeutic efficacy for MetS-associated DN, mitigating metabolic disturbances and enhancing renal health by modulating inflammatory and oxidative responses.
Keywords: GCG; diabetic nephropathy; metabolic syndrome; renal transcriptome analysis.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors affirm that there are no competing interests to disclose.
Figures
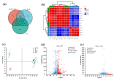
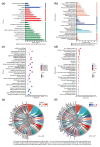
References
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

