Effects of Akt Activator SC79 on Human M0 Macrophage Phagocytosis and Cytokine Production
- PMID: 38891035
- PMCID: PMC11171788
- DOI: 10.3390/cells13110902
Effects of Akt Activator SC79 on Human M0 Macrophage Phagocytosis and Cytokine Production
Abstract
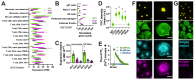
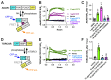
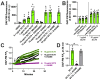
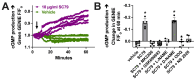
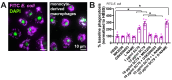
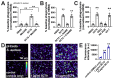
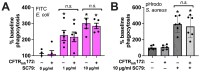
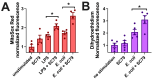
Akt is an important kinase in metabolism. Akt also phosphorylates and activates endothelial and neuronal nitric oxide (NO) synthases (eNOS and nNOS, respectively) expressed in M0 (unpolarized) macrophages. We showed that e/nNOS NO production downstream of bitter taste receptors enhances macrophage phagocytosis. In airway epithelial cells, we also showed that the activation of Akt by a small molecule (SC79) enhances NO production and increases levels of nuclear Nrf2, which reduces IL-8 transcription during concomitant stimulation with Toll-like receptor (TLR) 5 agonist flagellin. We hypothesized that SC79's production of NO in macrophages might likewise enhance phagocytosis and reduce the transcription of some pro-inflammatory cytokines. Using live cell imaging of fluorescent biosensors and indicator dyes, we found that SC79 induces Akt activation, NO production, and downstream cGMP production in primary human M0 macrophages. This was accompanied by a reduction in IL-6, IL-8, and IL-12 production during concomitant stimulation with bacterial lipopolysaccharide, an agonist of pattern recognition receptors including TLR4. Pharmacological inhibitors suggested that this effect was dependent on Akt and Nrf2. Together, these data suggest that several macrophage immune pathways are regulated by SC79 via Akt. A small-molecule Akt activator may be useful in some infection settings, warranting future in vivo studies.
Keywords: Toll-like receptor; inflammation; innate immunity; live cell imaging; monocyte-derived macrophages; signal transduction.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript; or in the decision to publish the results.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Small-molecule Akt-activation in airway cells induces NO production and reduces IL-8 transcription through Nrf-2.Respir Res. 2021 Oct 19;22(1):267. doi: 10.1186/s12931-021-01865-y. Respir Res. 2021. PMID: 34666758 Free PMC article.
-
Bitter taste receptors stimulate phagocytosis in human macrophages through calcium, nitric oxide, and cyclic-GMP signaling.Cell Mol Life Sci. 2021 Jan;78(1):271-286. doi: 10.1007/s00018-020-03494-y. Epub 2020 Mar 14. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2021. PMID: 32172302 Free PMC article.
-
HSP90 Modulates T2R Bitter Taste Receptor Nitric Oxide Production and Innate Immune Responses in Human Airway Epithelial Cells and Macrophages.Cells. 2022 Apr 27;11(9):1478. doi: 10.3390/cells11091478. Cells. 2022. PMID: 35563784 Free PMC article.
-
Genetic and Epigenetic Regulation of the Innate Immune Response to Gout.Immunol Invest. 2023 Apr;52(3):364-397. doi: 10.1080/08820139.2023.2168554. Epub 2023 Feb 6. Immunol Invest. 2023. PMID: 36745138 Review.
-
Postprandial lipoproteins and the molecular regulation of vascular homeostasis.Prog Lipid Res. 2013 Oct;52(4):446-64. doi: 10.1016/j.plipres.2013.06.001. Epub 2013 Jun 15. Prog Lipid Res. 2013. PMID: 23774609 Review.
Cited by
-
Bupivacaine Reduces the Viability of SH-SY5Y Cells and Promotes Apoptosis by the Inhibition of Akt Signaling Pathway.Neurochem Res. 2025 Apr 12;50(2):143. doi: 10.1007/s11064-025-04386-y. Neurochem Res. 2025. PMID: 40220051
-
Bioinformatics Approach to Identifying Molecular Targets of Isoliquiritigenin Affecting Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease: A Machine Learning Pharmacology Study.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 Apr 21;26(8):3907. doi: 10.3390/ijms26083907. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 40332792 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

