NLRX1 Mediates the Disruption of Intestinal Mucosal Function Caused by Porcine Astrovirus Infection via the Extracellular Regulated Protein Kinases/Myosin Light-Chain Kinase (ERK/MLCK) Pathway
- PMID: 38891045
- PMCID: PMC11171766
- DOI: 10.3390/cells13110913
NLRX1 Mediates the Disruption of Intestinal Mucosal Function Caused by Porcine Astrovirus Infection via the Extracellular Regulated Protein Kinases/Myosin Light-Chain Kinase (ERK/MLCK) Pathway
Abstract
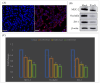
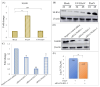
Porcine astrovirus (PAstV) has a potential zoonotic risk, with a high proportion of co-infection occurring with porcine epidemic diarrhea virus (PEDV) and other diarrheal pathogens. Despite its high prevalence, the cellular mechanism of PAstV pathogenesis is ill-defined. Previous proteomics analyses have revealed that the differentially expressed protein NOD-like receptor X1 (NLRX1) located in the mitochondria participates in several important antiviral signaling pathways in PAstV-4 infection, which are closely related to mitophagy. In this study, we confirmed that PAstV-4 infection significantly up-regulated NLRX1 and mitophagy in Caco-2 cells, while the silencing of NLRX1 or the treatment of mitophagy inhibitor 3-MA inhibited PAstV-4 replication. Additionally, PAstV-4 infection triggered the activation of the extracellular regulated protein kinases/ myosin light-chain kinase (ERK/MLCK) pathway, followed by the down-regulation of tight-junction proteins (occludin and ZO-1) as well as MUC-2 expression. The silencing of NLRX1 or the treatment of 3-MA inhibited myosin light-chain (MLC) phosphorylation and up-regulated occludin and ZO-1 proteins. Treatment of the ERK inhibitor PD98059 also inhibited MLC phosphorylation, while MLCK inhibitor ML-7 mitigated the down-regulation of mucosa-related protein expression induced by PAstV-4 infection. Yet, adding PD98059 or ML-7 did not affect NLRX1 expression. In summary, this study preliminarily explains that NLRX1 plays an important role in the disruption of intestinal mucosal function triggered by PAstV-4 infection via the ERK/MLC pathway. It will be helpful for further antiviral drug target screening and disease therapy.
Keywords: ERK/MLCK; NLRX1; intestinal mucosal barrier; mitophagy; porcine astrovirus.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures



References
-
- Bridger J.C. Detection by electron microscopy of caliciviruses, astroviruses and rotavirus–like particles in the faeces of piglets with diarrhoea. Vet. Rec. 1980;107:532–533. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

