The Impact of Natriuretic Peptides on Heart Development, Homeostasis, and Disease
- PMID: 38891063
- PMCID: PMC11172276
- DOI: 10.3390/cells13110931
The Impact of Natriuretic Peptides on Heart Development, Homeostasis, and Disease
Abstract
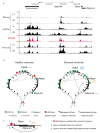
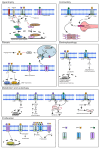
During mammalian heart development, the clustered genes encoding peptide hormones, Natriuretic Peptide A (NPPA; ANP) and B (NPPB; BNP), are transcriptionally co-regulated and co-expressed predominately in the atrial and ventricular trabecular cardiomyocytes. After birth, expression of NPPA and a natural antisense transcript NPPA-AS1 becomes restricted to the atrial cardiomyocytes. Both NPPA and NPPB are induced by cardiac stress and serve as markers for cardiovascular dysfunction or injury. NPPB gene products are extensively used as diagnostic and prognostic biomarkers for various cardiovascular disorders. Membrane-localized guanylyl cyclase receptors on many cell types throughout the body mediate the signaling of the natriuretic peptide ligands through the generation of intracellular cGMP, which interacts with and modulates the activity of cGMP-activated kinase and other enzymes and ion channels. The natriuretic peptide system plays a fundamental role in cardio-renal homeostasis, and its potent diuretic and vasodilatory effects provide compensatory mechanisms in cardiac pathophysiological conditions and heart failure. In addition, both peptides, but also CNP, have important intracardiac actions during heart development and homeostasis independent of the systemic functions. Exploration of the intracardiac functions may provide new leads for the therapeutic utility of natriuretic peptide-mediated signaling in heart diseases and rhythm disorders. Here, we review recent insights into the regulation of expression and intracardiac functions of NPPA and NPPB during heart development, homeostasis, and disease.
Keywords: cardiac disease; cardiac homeostasis; heart development; natriuretic peptides.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Mukoyama M., Nakao K., Hosoda K., Suga S., Saito Y., Ogawa Y., Shirakami G., Jougasaki M., Obata K., Yasue H., et al. Brain natriuretic peptide as a novel cardiac hormone in humans. Evidence for an exquisite dual natriuretic peptide system, atrial natriuretic peptide and brain natriuretic peptide. J. Clin. Investig. 1991;87:1402–1412. doi: 10.1172/jci115146. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

