Regulator of Lipid Metabolism NHR-49 Mediates Pathogen Avoidance through Precise Control of Neuronal Activity
- PMID: 38891110
- PMCID: PMC11172349
- DOI: 10.3390/cells13110978
Regulator of Lipid Metabolism NHR-49 Mediates Pathogen Avoidance through Precise Control of Neuronal Activity
Abstract
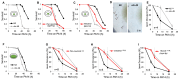
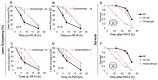
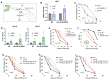
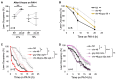
Precise control of neuronal activity is crucial for the proper functioning of neurons. How lipid homeostasis contributes to neuronal activity and how much of it is regulated by cells autonomously is unclear. In this study, we discovered that absence of the lipid regulator nhr-49, a functional ortholog of the peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor (PPAR) in Caenorhabditis elegans, resulted in defective pathogen avoidance behavior against Pseudomonas aeruginosa (PA14). Functional NHR-49 was required in the neurons, and more specifically, in a set of oxygen-sensing body cavity neurons, URX, AQR, and PQR. We found that lowering the neuronal activity of the body cavity neurons improved avoidance in nhr-49 mutants. Calcium imaging in URX neurons showed that nhr-49 mutants displayed longer-lasting calcium transients in response to an O2 upshift, suggesting that excess neuronal activity leads to avoidance defects. Cell-specific rescue of NHR-49 in the body cavity neurons was sufficient to improve pathogen avoidance, as well as URX neuron calcium kinetics. Supplementation with oleic acid also improved avoidance behavior and URX calcium kinetics, suggesting that the defective calcium response in the neuron is due to lipid dysfunction. These findings highlight the role of cell-autonomous lipid regulation in neuronal physiology and immune behavior.
Keywords: Caenorhabditis elegans; PPAR; Pseudomonas aeruginosa; immune behavior; lipid metabolism; neuron.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Loss of cilia in chemosensory neurons inhibits pathogen avoidance in Caenorhabditis elegans.Microbes Infect. 2024 Nov-Dec;26(8):105370. doi: 10.1016/j.micinf.2024.105370. Epub 2024 Jun 4. Microbes Infect. 2024. PMID: 38843949
-
NHR-49 Transcription Factor Regulates Immunometabolic Response and Survival of Caenorhabditis elegans during Enterococcus faecalis Infection.Infect Immun. 2020 Jul 21;88(8):e00130-20. doi: 10.1128/IAI.00130-20. Print 2020 Jul 21. Infect Immun. 2020. PMID: 32482643 Free PMC article.
-
Repression of a potassium channel by nuclear hormone receptor and TGF-β signaling modulates insulin signaling in Caenorhabditis elegans.PLoS Genet. 2012;8(2):e1002519. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1002519. Epub 2012 Feb 16. PLoS Genet. 2012. PMID: 22359515 Free PMC article.
-
NHR-85 modulates mitochondrial and lipid homeostasis to protect against α-synuclein aggregation in C. elegans.J Cell Sci. 2025 May 1;138(9):jcs263651. doi: 10.1242/jcs.263651. Epub 2025 May 9. J Cell Sci. 2025. PMID: 40211924
-
O2-sensing neurons control CO2 response in C. elegans.J Neurosci. 2013 Jun 5;33(23):9675-83. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.4541-12.2013. J Neurosci. 2013. PMID: 23739964 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Nuclear Hormone Receptor NHR-49/HNF4α Couples Fertility Regulation to Resource Allocation and Longevity in C. elegans.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2025 Jul 18:2025.07.14.664468. doi: 10.1101/2025.07.14.664468. bioRxiv. 2025. PMID: 40791495 Free PMC article. Preprint.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

