Conditional Knockout of Neurexins Alters the Contribution of Calcium Channel Subtypes to Presynaptic Ca2+ Influx
- PMID: 38891114
- PMCID: PMC11171642
- DOI: 10.3390/cells13110981
Conditional Knockout of Neurexins Alters the Contribution of Calcium Channel Subtypes to Presynaptic Ca2+ Influx
Abstract
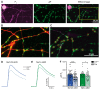
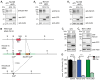
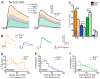
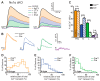
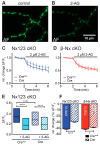
Presynaptic Ca2+ influx through voltage-gated Ca2+ channels (VGCCs) is a key signal for synaptic vesicle release. Synaptic neurexins can partially determine the strength of transmission by regulating VGCCs. However, it is unknown whether neurexins modulate Ca2+ influx via all VGCC subtypes similarly. Here, we performed live cell imaging of synaptic boutons from primary hippocampal neurons with a Ca2+ indicator. We used the expression of inactive and active Cre recombinase to compare control to conditional knockout neurons lacking either all or selected neurexin variants. We found that reduced total presynaptic Ca2+ transients caused by the deletion of all neurexins were primarily due to the reduced contribution of P/Q-type VGCCs. The deletion of neurexin1α alone also reduced the total presynaptic Ca2+ influx but increased Ca2+ influx via N-type VGCCs. Moreover, we tested whether the decrease in Ca2+ influx induced by activation of cannabinoid receptor 1 (CB1-receptor) is modulated by neurexins. Unlike earlier observations emphasizing a role for β-neurexins, we found that the decrease in presynaptic Ca2+ transients induced by CB1-receptor activation depended more strongly on the presence of α-neurexins in hippocampal neurons. Together, our results suggest that neurexins have unique roles in the modulation of presynaptic Ca2+ influx through VGCC subtypes and that different neurexin variants may affect specific VGCCs.
Keywords: calcium channel subtypes; endocannabinoid system; genetically encoded calcium indicator; neurexin; presynapse.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Nakamura Y., Harada H., Kamasawa N., Matsui K., Rothman J.S., Shigemoto R., Silver R.A., DiGregorio D.A., Takahashi T. Nanoscale distribution of presynaptic Ca2+ channels and its impact on vesicular release during development. Neuron. 2015;85:145–158. doi: 10.1016/j.neuron.2014.11.019. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

