Integrating NDVI, SPAD, and Canopy Temperature for Strategic Nitrogen and Seeding Rate Management to Enhance Yield, Quality, and Sustainability in Wheat Cultivation
- PMID: 38891382
- PMCID: PMC11174591
- DOI: 10.3390/plants13111574
Integrating NDVI, SPAD, and Canopy Temperature for Strategic Nitrogen and Seeding Rate Management to Enhance Yield, Quality, and Sustainability in Wheat Cultivation
Abstract
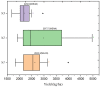
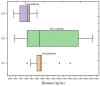
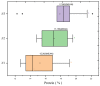
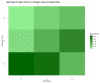
This study explores the interplay between nitrogen doses and seeding rates on wheat yield, biomass, and protein content. Utilizing tools such as the Normalized Difference Vegetation Index (NDVI), Soil Plant Analysis Development (SPAD) measurements, and canopy temperature (CT), we conducted experiments over five growing seasons. The treatments included three nitrogen levels (0, 60, 120 kg/ha) and three seeding rates (300, 400, 500 seeds/m2) in a split-plot design with 90 plots and two replications. Our results show that an intermediate nitrogen dose (60 kg/ha) combined with a moderate seed rate (400 seeds/m2) enhances wheat yield by 22.95%. Reduced nitrogen levels increased protein content, demonstrating wheat's adaptive mechanisms under nitrogen constraints. NDVI analysis highlighted significant growth during the tillering phase with high nitrogen, emphasizing early-stage nutrient management. SPAD measurements showed that early nitrogen applications boost chlorophyll content, essential for vigorous early growth, while CT data indicate that optimal nitrogen and seed rates can effectively modulate plant stress responses. As crops mature, the predictive capacity of NDVI declines, indicating the need for adjusted nitrogen strategies. Collectively, these findings advocate for refined management of nitrogen and seeding rates, integrating NDVI, SPAD, and CT assessments to enhance yields and promote sustainable agricultural practices while minimizing environmental impacts.
Keywords: biomass; chlorophyll measurement; nitrogen efficiency; protein content; remote sensing; seeding strategy; wheat growth; yield.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures










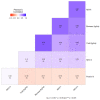



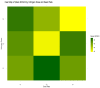
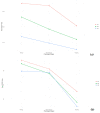

References
-
- Kizilgeci F., Yildirim M., Islam M.S., Ratnasekera D., Iqbal M.A., Sabagh A.E. Normalized difference vegetation index and chlorophyll content for precision nitrogen management in durum wheat cultivars under semi-arid conditions. Sustainability. 2021;13:3725. doi: 10.3390/su13073725. - DOI
-
- Yin Q., Zhang Y., Li W., Wang J., Wang W., Ahmad I., Zhou G., Huo Z. Better inversion of wheat canopy SPAD values before heading stage using spectral and texture indices based on UAV multispectral imagery. Remote Sens. 2023;15:4935. doi: 10.3390/rs15204935. - DOI
-
- Cavalaris C., Megoudi S., Maxouri M., Anatolitis K., Sifakis M., Levizou E., Kyparissis A. Modeling of durum wheat yield based on sentinel-2 imagery. Agronomy. 2021;11:1486. doi: 10.3390/agronomy11081486. - DOI
-
- Pampana S., Mariotti M. Durum wheat yield and N uptake as affected by N source, timing, and rate in two mediterranean environments. Agronomy. 2021;11:1299. doi: 10.3390/agronomy11071299. - DOI
-
- Tedone L., Ali S.A., Verdini L., De Mastro G. Nitrogen management strategy for optimizing agronomic and environmental performance of rainfed durum wheat under Mediterranean climate. J. Clean. Prod. 2018;172:2058–2074. doi: 10.1016/j.jclepro.2017.11.215. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

