Inherited Structure Properties of Larch Arabinogalactan Affected via the TEMPO/NaBr/NaOCl Oxidative System
- PMID: 38891405
- PMCID: PMC11175108
- DOI: 10.3390/polym16111458
Inherited Structure Properties of Larch Arabinogalactan Affected via the TEMPO/NaBr/NaOCl Oxidative System
Abstract
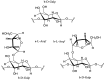
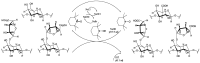
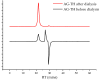
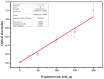
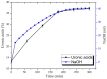
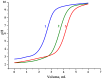
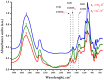
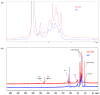
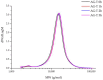
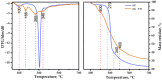
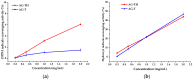
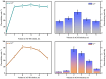
Arabinogalactan (AG), extracted from larch wood, is a β-1,3-galactan backbone and β-1,6-galactan side chains with attached α-1-arabinofuranosyl and β-1-arabinopyranosyl residues. Although the structural characteristics of arabinogalactan II type have already been studied, its functionalization using 2,2,6,6-tetramethylpiperidin-1-oxyl (TEMPO) oxidation remains a promising avenue. In this study, the oxidation of AG, a neutral polysaccharide, was carried out using the TEMPO/NaBr/NaOCl system, resulting in polyuronides with improved functional properties. The oxidation of AG was controlled by analyzing portions of the reaction mixture using spectrophotometric and titration methods. To determine the effect of the TEMPO/NaBr/NaOCl system, air-dried samples of native and oxidized AG were studied by Fourier-transform infrared (FTIR) and nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) spectroscopy, as well as by gel permeation chromatography. Compounds that model free (1,1-diphenyl-2-picrylhydrazyl (DPPH)) and hydroxyl radicals (iron(II) sulfate, hydrogen peroxide, and salicylic acid) were used to study the antioxidant properties. It was found that, in oxidized forms of AG, the content of carboxyl groups increases by 0.61 mmol compared to native AG. The transformation of oxidized AG into the H+ form using a strong acid cation exchanger leads to an increase in the number of active carboxyl groups to 0.76 mmol. Using FTIR spectroscopy, characteristic absorption bands (1742, 1639, and 1403 cm-1) were established, indicating the occurrence of oxidative processes with a subsequent reduction in the carboxyl group. The functionality of AG was also confirmed by gel permeation chromatography (GPC), which is reflected in an increase in molecular weights (up to 15,700 g/mol). A study of the antioxidant properties of the oxidized and protonated forms of AG show that the obtained antioxidant activity (AOA) values are generally characteristic of polyuronic acids. Therefore, the TEMPO oxidation of AG and other neutral polysaccharides can be considered a promising approach for obtaining compounds with the necessary controlled characteristics.
Keywords: 2,2,6,6-tetramethylpiperidin-1-oxyl (TEMPO); arabinogalactan; flocculation; larch; oxidation.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures



Similar articles
-
TEMPO-Oxidized Spruce Galactoglucomannan-Biopolymer with Enhanced Antioxidant Activity and Selective Heavy-Metal Sorption.Antioxidants (Basel). 2025 May 9;14(5):569. doi: 10.3390/antiox14050569. Antioxidants (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40427450 Free PMC article.
-
Yariv reactivity of type II arabinogalactan from larch wood.Carbohydr Res. 2018 Sep;467:8-13. doi: 10.1016/j.carres.2018.07.004. Epub 2018 Jul 7. Carbohydr Res. 2018. PMID: 30036728
-
TEMPO/NaClO2/NaOCl oxidation of arabinoxylans.Carbohydr Polym. 2021 May 1;259:117781. doi: 10.1016/j.carbpol.2021.117781. Epub 2021 Feb 9. Carbohydr Polym. 2021. PMID: 33674018
-
Larch arabinogalactan: clinical relevance of a novel immune-enhancing polysaccharide.Altern Med Rev. 1999 Apr;4(2):96-103. Altern Med Rev. 1999. PMID: 10231609 Review.
-
Plant type II arabinogalactan: Structural features and modification to increase functionality.Carbohydr Res. 2023 Jul;529:108828. doi: 10.1016/j.carres.2023.108828. Epub 2023 May 2. Carbohydr Res. 2023. PMID: 37182471 Review.
Cited by
-
TEMPO-Oxidized Spruce Galactoglucomannan-Biopolymer with Enhanced Antioxidant Activity and Selective Heavy-Metal Sorption.Antioxidants (Basel). 2025 May 9;14(5):569. doi: 10.3390/antiox14050569. Antioxidants (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40427450 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Huang W., Xie Y., Guo T., Dai W., Nan L., Wang Q., Liu Y., Lan W., Wang Z., Huang L., et al. A new perspective on structural characterisation and immunomodulatory activity of arabinogalactan in Larix kaempferi from Qinling Mountains. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2024;265:130859. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2024.130859. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Goellner E.M., Utermoehlen J., Kramer R., Classen B. Structure of arabinogalactan from Larix laricina and its reactivity with antibodies directed against type-II-arabinogalactans. Carbohydr. Polym. 2011;86:1739–1744. doi: 10.1016/j.carbpol.2011.07.006. - DOI
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

