Laboratory and Numerical Investigation of Pre-Tensioned Reinforced Concrete Railway Sleepers Combined with Plastic Fiber Reinforcement
- PMID: 38891445
- PMCID: PMC11174923
- DOI: 10.3390/polym16111498
Laboratory and Numerical Investigation of Pre-Tensioned Reinforced Concrete Railway Sleepers Combined with Plastic Fiber Reinforcement
Abstract
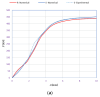
This research investigates the application of plastic fiber reinforcement in pre-tensioned reinforced concrete railway sleepers, conducting an in-depth examination in both experimental and computational aspects. Utilizing 3-point bending tests and the GOM ARAMIS system for Digital Image Correlation, this study meticulously evaluates the structural responses and crack development in conventional and plastic fiber-reinforced sleepers under varying bending moments. Complementing these tests, the investigation employs ABAQUS' advanced finite element modeling to enhance the analysis, ensuring precise calibration and validation of the numerical models. This dual approach comprehensively explains the mechanical behavior differences and stresses within the examined structures. The incorporation of plastic fibers not only demonstrates a significant improvement in mechanical strength and crack resistance but paves the way for advancements in railway sleeper technology. By shedding light on the enhanced durability and performance of reinforced concrete structures, this study makes a significant contribution to civil engineering materials science, highlighting the potential for innovative material applications in the construction industry.
Keywords: ABAQUS; DIC; FEM; laboratory experiments; numerical modeling; plastic fiber reinforcement; pre-stressing; railway; reinforced concrete; sleeper.
Conflict of interest statement
Author László Gáspár was employed by the company KTI Institute for Transport Sciences Non-Profit Ltd. The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures










References
-
- Yu Z., Lanre Ridwan I., Irshad A.U.R., Tanveer M., Khan S.A.R. Investigating the Nexuses between Transportation Infrastructure, Renewable Energy Sources, and Economic Growth: Striving towards Sustainable Development. Ain Shams Eng. J. 2023;14:101843. doi: 10.1016/j.asej.2022.101843. - DOI
-
- Healey K.T. Transportation as a Factor in Economic Growth. J. Econ. Hist. 1947;7:72–88. doi: 10.1017/S0022050700065232. - DOI
-
- Dickinson H.W. A Short History of the Steam Engine. Volume 9780429423 Routledge; London, UK: 2022.
-
- Czére B. A Vasút Története (The History of Railway) Corvina Kiadó; Budapest, Hungary: 1989. (In Hungarian)
-
- Ramazan B., Mussaliyeva R., Bitileuova Z., Naumov V., Taran I. Choosing the Logistics Chain Structure for Deliveries of Bulk Loads: Case Study of the Republic Kazakhstan. Nauk. Visnyk Natsionalnoho Hirnychoho Universytetu. 2021;2021:142–147. doi: 10.33271/nvngu/2021-3/142. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

