Surface Evolution of Polymer Films Grown by Vapor Deposition: Growth of Local and Global Slopes of Interfaces
- PMID: 38891479
- PMCID: PMC11175125
- DOI: 10.3390/polym16111535
Surface Evolution of Polymer Films Grown by Vapor Deposition: Growth of Local and Global Slopes of Interfaces
Abstract
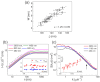
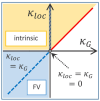
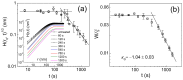
The kinetic roughening of polymer films grown by vapor deposition polymerization was analyzed using the widely accepted classification framework of "generic scaling ansatz" given for the structure factor. Over the past two decades, this method has played a pivotal role in classifying diverse forms of dynamic scaling and understanding the mechanisms driving interface roughening. The roughness exponents of the polymer films were consistently determined as α=1.25±0.09, αloc=0.73±0.02, and αs=0.99±0.06. However, the inability to unambiguously assign these roughness exponent values to a specific scaling subclass prompts the proposal of a practical alternative. This report illustrates how all potential dynamic scaling can be consistently identified and classified based on the relationship between two temporal scaling exponents measured in real space: the average local slope and the global slope of the interface. The intrinsic anomalous roughening class is conclusively assigned to polymer film growth characterized by anomalous "native (background slope-removed) local height fluctuations". Moreover, the new analysis reveals that interfaces exhibiting anomalous scaling, previously classified as intrinsic anomalous roughening, could potentially belong to the super-rough class, particularly when the spectral roughness exponent αs is equal to 1.
Keywords: atomic force microscopy; kinetic roughening; polymer film growth; surface roughness; vapor deposition polymerization.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures



References
-
- Barabási A.-L., Stanley H.E. Fractal Concepts in Surface Growth. Cambridge University Press; New York, NY, USA: 1995.
-
- Krug J. Origins of scale invariance in growth processes. Adv. Phys. 1997;46:139–282. doi: 10.1080/00018739700101498. - DOI
-
- Family F., Vicsek T. Scaling of the active zone in the Eden process on percolation networks and the ballistic deposition model. J. Phys. A. 1985;18:L75–L81. doi: 10.1088/0305-4470/18/2/005. - DOI
-
- Wolf D.E., Villain J. Growth with surface diffusion. Europhys. Lett. 1990;13:389–394. doi: 10.1209/0295-5075/13/5/002. - DOI
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

