Influence of Cutting Regime Parameters on Determining the Main Cutting Resistance during Polypropylene Machining
- PMID: 38891483
- PMCID: PMC11175104
- DOI: 10.3390/polym16111537
Influence of Cutting Regime Parameters on Determining the Main Cutting Resistance during Polypropylene Machining
Abstract
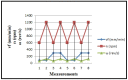
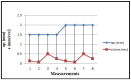
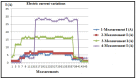
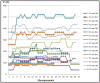
This study examines the impact of cutting regimes on determining cutting resistance in the processing of polypropylene (PP) using the CNC lathe EMCO F5. The rationale for this research stems from polypropylene's rarity among thermoplastics in possessing structural stability, allowing for its comparison to metals and practical application in products replacing metal parts. Leveraging its favorable mechanical properties, polypropylene finds utility in producing parts subject to dynamic loads, boasting high resistance to impact loads-particularly undesirable in machining. An advantageous characteristic of polypropylene is its affordability, rendering it an economical choice across numerous applications. Despite these merits, polypropylene's exploration in cutting processing remains limited, underscoring the novelty of this research endeavor. The main method for determining cutting resistance involves measuring electric current strength during processing. This direct measurement, facilitated by input cutting regime parameters, is recorded by the PLC controller, with the current value extracted from the machine tool's ammeter. The experimental approach entails varying cutting regime parameters-cutting speed (v), feed rate (s), and depth of cut (a)-across minimum and maximum values, recognized as pivotal factors influencing cutting force development and the attainment of the desired machined surface quality.
Keywords: CNC lathe; PLC; cutting resistance; machining; manufacturing efficiency; polypropylene.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures










Similar articles
-
Computational Analysis of Machining Induced Stress Distribution during Dry and Cryogenic Orthogonal Cutting of 7075 Aluminium Closed Cell Syntactic Foams.Micromachines (Basel). 2023 Jan 10;14(1):174. doi: 10.3390/mi14010174. Micromachines (Basel). 2023. PMID: 36677235 Free PMC article.
-
An Experimental Investigation on Micro End Milling with High-Speed Up Cut Milling for Hardened Die Steel.Materials (Basel). 2020 Oct 23;13(21):4745. doi: 10.3390/ma13214745. Materials (Basel). 2020. PMID: 33114162 Free PMC article.
-
Influence of Machining Parameters on Cutting and Chip-Formation Process during Cortical Bone Orthogonal Machining.Materials (Basel). 2022 Sep 15;15(18):6414. doi: 10.3390/ma15186414. Materials (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36143728 Free PMC article.
-
Cutting Forces Assessment in CNC Machining Processes: A Critical Review.Sensors (Basel). 2020 Aug 13;20(16):4536. doi: 10.3390/s20164536. Sensors (Basel). 2020. PMID: 32823686 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A Comparative Review of Thermocouple and Infrared Radiation Temperature Measurement Methods during the Machining of Metals.Sensors (Basel). 2022 Jun 22;22(13):4693. doi: 10.3390/s22134693. Sensors (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35808192 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Ljevar A., Rancic M. Processing of Plastics Cutting and Surface Roughness, Materials from Conference Proceedings, XV Jupiter; Proceedings of the Materials from Conference Proceedings; Jupiter, Cavtat, Croatia. 1989; pp. 101–105.
-
- Dutta H., Debnath K., Sarma D.K. A Study of Material Removal and Surface Characteristics in Micro-electrical Discharge Machining of Carbon Fiber-reinforced Plastics. Polym. Compos. 2019;40:4033–4041. doi: 10.1002/pc.25264. - DOI
-
- Xu J., Huang X., Davim J.P., Ji M., Chen M. On the Machining Behavior of Carbon Fiber Reinforced Polyimide and PEEK Thermoplastic Composites. Polym. Compos. 2020;41:3649–3663. doi: 10.1002/pc.25663. - DOI
-
- Nagel T. Complete Solutions for Plastics Processing: Faster and More Precise with Portal Milling Machine; 161. Volume 1–2 VDI-Z Integrierte Produktion; Eltville, Germany: 2019.
-
- Mallick P.S., Pratap A., Patra K. Review on Cryogenic Assisted Micro-Machining of Soft Polymer: An Emphasis on Molecular Physics, Chamber Design, Performance Analysis and Sustainability. J. Manuf. Process. 2022;80:930–957. doi: 10.1016/j.jmapro.2022.06.035. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

