Stability and Biaxial Behavior of Fresh Cheese Coated with Nanoliposomes Encapsulating Grape Seed Tannins and Polysaccharides Using Immersion and Spray Methods
- PMID: 38891503
- PMCID: PMC11174876
- DOI: 10.3390/polym16111559
Stability and Biaxial Behavior of Fresh Cheese Coated with Nanoliposomes Encapsulating Grape Seed Tannins and Polysaccharides Using Immersion and Spray Methods
Abstract
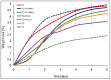
In the food industry context, where fresh cheese stands out as a highly perishable product with a short shelf life, this study aimed to extend its preservation through multi-layer edible coatings. The overall objective was to analyze the biaxial behavior and texture of fresh cheese coated with nanoliposomes encapsulating grape seed tannins (NTs) and polysaccharides (hydroxypropyl methylcellulose; HPMC and kappa carrageenan; KC) using immersion and spray methods, establishing comparisons with uncoated cheeses and commercial samples, including an accelerated shelf-life study. NT, HPMC, and KC were employed as primary components in the multi-layer edible coatings, which were applied through immersion and spray. The results revealed significant improvements, such as a 20% reduction in weight loss and increased stability against oxidation, evidenced by a 30% lower peroxide index than the uncoated samples. These findings underscore the effectiveness of edible coatings in enhancing the quality and extending the shelf life of fresh cheese, highlighting the innovative application of nanoliposomes and polysaccharide blends and the relevance of applying this strategy in the food industry. In conclusion, this study provides a promising perspective for developing dairy products with improved properties, opening opportunities to meet market demands and enhance consumer acceptance.
Keywords: biaxial viscosity; cheese; nanoliposomes; tannins; texture.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest. The funders had no role in the study’s design; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript; or in the decision to publish the results.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Mechanical and Surface Properties of Edible Coatings Elaborated with Nanoliposomes Encapsulating Grape Seed Tannins and Polysaccharides.Polymers (Basel). 2023 Sep 15;15(18):3774. doi: 10.3390/polym15183774. Polymers (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37765628 Free PMC article.
-
Spray technology applications of xanthan gum-based edible coatings for fresh-cut lotus root (Nelumbo nucifera).Food Res Int. 2020 Nov;137:109723. doi: 10.1016/j.foodres.2020.109723. Epub 2020 Sep 19. Food Res Int. 2020. PMID: 33233292
-
Physicochemical Properties of Nanoliposomes Encapsulating Grape Seed Tannins Formed with Ultrasound Cycles.Foods. 2024 Jan 27;13(3):414. doi: 10.3390/foods13030414. Foods. 2024. PMID: 38338549 Free PMC article.
-
Combining edible coatings technology and nanoencapsulation for food application: A brief review with an emphasis on nanoliposomes.Food Res Int. 2021 Jul;145:110402. doi: 10.1016/j.foodres.2021.110402. Epub 2021 May 11. Food Res Int. 2021. PMID: 34112405 Review.
-
Use of edible films and coatings in cheese preservation: Opportunities and challenges.Food Res Int. 2018 May;107:84-92. doi: 10.1016/j.foodres.2018.02.013. Epub 2018 Feb 4. Food Res Int. 2018. PMID: 29580546 Review.
References
-
- Vasiliauskaite A., Mileriene J., Songisepp E., Rud I., Muizniece-Brasava S., Ciprovica I., Axelsson L., Lutter L., Aleksandrovas E., Tammsaar E., et al. Application of edible coating based on liquid acid whey protein concentrate with indigenous Lactobacillus helveticus for acid-curd cheese quality improvement. Foods. 2022;11:3353. doi: 10.3390/foods11213353. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Duarte R.V., Casal S., Gomes A.M., Delgadillo I., Saraiva J.A. Nutritional and quality evaluation of hyperbaric stored fresh cheeses. Food Chem. Adv. 2023;2:100212. doi: 10.1016/j.focha.2023.100212. - DOI
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

