DFT and TD-DFT Investigations for the Limitations of Lengthening the Polyene Bridge between N,N-dimethylanilino Donor and Dicyanovinyl Acceptor Molecules as a D-π-A Dye-Sensitized Solar Cell
- PMID: 38891775
- PMCID: PMC11172313
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms25115586
DFT and TD-DFT Investigations for the Limitations of Lengthening the Polyene Bridge between N,N-dimethylanilino Donor and Dicyanovinyl Acceptor Molecules as a D-π-A Dye-Sensitized Solar Cell
Abstract
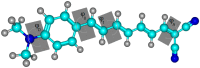
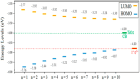
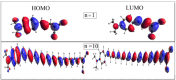
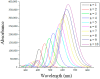
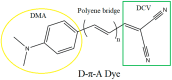
One useful technique for increasing the efficiency of organic dye-sensitized solar cells (DSSCs) is to extend the π-conjugated bridges between the donor (D) and the acceptor (A) units. The present study used the DFT and TD-DFT techniques to investigate the effect of lengthening the polyene bridge between the donor N, N-dimethyl-anilino and the acceptor dicyanovinyl. The results of the calculated key properties were not all in line with expectations. Planar structure was associated with increasing the π-conjugation linker, implying efficient electron transfer from the donor to the acceptor. A smaller energy gap, greater oscillator strength values, and red-shifted electronic absorption were also observed when the number of polyene units was increased. However, some results indicated that the potential of the stated dyes to operate as effective dye-sensitized solar cells is limited when the polyene bridge is extended. Increasing the polyene units causes the HOMO level to rise until it exceeds the redox potential of the electrolyte, which delays regeneration and impedes the electron transport cycle from being completed. As the number of conjugated units increases, the terminal lobes of HOMO and LUMO continue to shrink, which affects the ease of intramolecular charge transfer within the dyes. Smaller polyene chain lengths yielded the most favorable results when evaluating the efficiency of electron injection and regeneration. This means that the charge transfer mechanism between the conduction band of the semiconductor and the electrolyte is not improved by extending the polyene bridge. The open circuit voltage (VOC) was reduced from 1.23 to 0.70 V. Similarly, the excited-state duration (τ) decreased from 1.71 to 1.23 ns as the number of polyene units increased from n = 1 to n = 10. These findings are incompatible with the power conversion efficiency requirements of DSSCs. Therefore, the elongation of the polyene bridge in such D-π-A configurations rules out its application in solar cell devices.
Keywords: D-π-A dye; DFT; TD–DFT; UV–Vis spectrum; photovoltaic properties; polyene bridge.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Kim J.-H., Kim D.-H., So J.-H., Koo H.-J. Toward Eco-Friendly Dye-Sensitized Solar Cells (DSSCs): Natural Dyes and Aqueous Electrolytes. Energies. 2021;15:219. doi: 10.3390/en15010219. - DOI
-
- Mariotti N., Bonomo M., Fagiolari L., Barbero N., Gerbaldi C., Bella F., Barolo C. Recent advances in eco-friendly and cost-effective materials towards sustainable dye-sensitized solar cells. Green Chem. 2020;22:7168–7218. doi: 10.1039/d0gc01148g. - DOI
-
- Andualem A., Demiss S. Review on Dye-Sensitized Solar Cells (DSSCs) J. Heterocycl. 2018;1:29–34. doi: 10.33805/2639-6734.103. - DOI
-
- Bhattacharya S., Datta J. Wide-low energy coupled semi-conductor layers of TiO2–CdX boosting the performance of DSSC. Sol. Energy. 2020;208:674–687. doi: 10.1016/j.solener.2020.08.024. - DOI
-
- Aslam A., Mehmood U., Arshad M.H., Ishfaq A., Zaheer J., Khan A.U.H., Sufyan M. Dye-sensitized solar cells (DSSCs) as a potential photovoltaic technology for the self-powered internet of things (IoTs) applications. Sol. Energy. 2020;207:874–892. doi: 10.1016/j.solener.2020.07.029. - DOI
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

