Clinical Significance of the Plasma Biomarker Panels in Amyloid-Negative and Tau PET-Positive Amnestic Patients: Comparisons with Alzheimer's Disease and Unimpaired Cognitive Controls
- PMID: 38891795
- PMCID: PMC11171590
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms25115607
Clinical Significance of the Plasma Biomarker Panels in Amyloid-Negative and Tau PET-Positive Amnestic Patients: Comparisons with Alzheimer's Disease and Unimpaired Cognitive Controls
Abstract
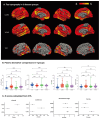
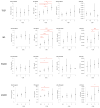
The purpose of this study was to investigate whether plasma biomarkers can help to diagnose, differentiate from Alzheimer disease (AD), and stage cognitive performance in patients with positron emission tomography (PET)-confirmed primary age-related tauopathy, termed tau-first cognitive proteinopathy (TCP) in this study. In this multi-center study, we enrolled 285 subjects with young-onset AD (YOAD; n = 55), late-onset AD (LOAD; n = 96), TCP (n = 44), and cognitively unimpaired controls (CTL; n = 90) and analyzed plasma Aβ42/Aβ40, pTau181, neurofilament light (NFL), and total-tau using single-molecule assays. Amyloid and tau centiloids reflected pathological burden, and hippocampal volume reflected structural integrity. Receiver operating characteristic curves and areas under the curves (AUCs) were used to determine the diagnostic accuracy of plasma biomarkers compared to hippocampal volume and amyloid and tau centiloids. The Mini-Mental State Examination score (MMSE) served as the major cognitive outcome. Logistic stepwise regression was used to assess the overall diagnostic accuracy, combining fluid and structural biomarkers and a stepwise linear regression model for the significant variables for MMSE. For TCP, tau centiloid reached the highest AUC for diagnosis (0.79), while pTau181 could differentiate TCP from YOAD (accuracy 0.775) and LOAD (accuracy 0.806). NFL reflected the clinical dementia rating in TCP, while pTau181 (rho = 0.3487, p = 0.03) and Aβ42/Aβ40 (rho = -0.36, p = 0.02) were significantly correlated with tau centiloid. Hippocampal volume (unstandardized β = 4.99, p = 0.01) outperformed all of the fluid biomarkers in predicting MMSE scores in the TCP group. Our results support the superiority of tau PET to diagnose TCP, pTau181 to differentiate TCP from YOAD or LOAD, and NFL for functional staging.
Keywords: florzolotau; pTau181; primary age-related tauopathy; tau first cognitive tauopathy.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Jack C.R., Jr., Bennett D.A., Blennow K., Carrillo M.C., Dunn B., Haeberlein S.B., Holtzman D.M., Jagust W., Jessen F., Karlawish J., et al. NIA-AA Research Framework: Toward a biological definition of Alzheimer’s disease. Alzheimer’s Dement. 2018;14:535–562. doi: 10.1016/j.jalz.2018.02.018. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Ashton N.J., Benedet A.L., Pascoal T.A., Karikari T.K., Lantero-Rodriguez J., Brum W.S., Mathotaarachchi S., Therriault J., Savard M., Chamoun M., et al. Cerebrospinal fluid p-tau231 as an early indicator of emerging pathology in Alzheimer’s disease. EBioMedicine. 2022;76:103836. doi: 10.1016/j.ebiom.2022.103836. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Olsson B., Lautner R., Andreasson U., Ohrfelt A., Portelius E., Bjerke M., Holtta M., Rosen C., Olsson C., Strobel G., et al. CSF and blood biomarkers for the diagnosis of Alzheimer’s disease: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Lancet Neurol. 2016;15:673–684. doi: 10.1016/S1474-4422(16)00070-3. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Bridel C., van Wieringen W.N., Zetterberg H., Tijms B.M., Teunissen C.E., The NFL Group. Alvarez-Cermeno J.C., Andreasson U., Axelsson M., Backstrom D.C., et al. Diagnostic Value of Cerebrospinal Fluid Neurofilament Light Protein in Neurology: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. JAMA Neurol. 2019;76:1035–1048. doi: 10.1001/jamaneurol.2019.1534. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

