Apple Glycosyltransferase MdUGT73AR4 Glycosylates ABA to Regulate Stomatal Movement Involved in Drought Stress
- PMID: 38891859
- PMCID: PMC11171509
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms25115672
Apple Glycosyltransferase MdUGT73AR4 Glycosylates ABA to Regulate Stomatal Movement Involved in Drought Stress
Abstract
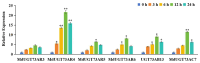
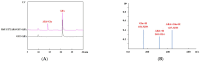
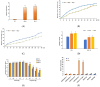
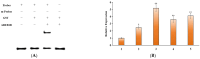
Abscisic acid (ABA) is a drought-stress-responsive hormone that plays an important role in the stomatal activity of plant leaves. Currently, ABA glycosides have been identified in apples, but their glycosyltransferases for glycosylation modification of ABA are still unidentified. In this study, the mRNA expression of glycosyltransferase gene MdUGT73AR4 was significantly up-regulated in mature apple leaves which were treated in drought stress by Real-Time PCR. It was hypothesised that MdUGT73AR4 might play an important role in drought stress. In order to further characterise the glycosylation modification substrate of glycosyltransferase MdUGT73AR4, we demonstrated through in vitro and in vivo functional validation that MdUGT73AR4 can glycosylate ABA. Moreover, the overexpression lines of MdUGT73AR4 significantly enhance its drought stress resistance function. We also found that the adversity stress transcription factor AREB1B might be an upstream transcription factor of MdUGT73AR4 by bioinformatics, EMSA, and ChIP experiments. In conclusion, this study found that the adversity stress transcription factor AREB1B was significantly up-regulated at the onset of drought stress, which in turn positively regulated the downstream glycosyltransferase MdUGT73AR4, causing it to modify ABA by mass glycosylation and promoting the ABA synthesis pathway, resulting in the accumulation of ABA content, and displaying a stress-resistant phenotype.
Keywords: ABA; AREB1B; MdUGT73AR4; drought tolerance; glycosyltransferase; stomatal.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Activation of the ABA Signal Pathway Mediated by GABA Improves the Drought Resistance of Apple Seedlings.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Nov 24;22(23):12676. doi: 10.3390/ijms222312676. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34884481 Free PMC article.
-
MdTCP46 interacts with MdABI5 to negatively regulate ABA signalling and drought response in apple.Plant Cell Environ. 2022 Nov;45(11):3233-3248. doi: 10.1111/pce.14429. Epub 2022 Sep 12. Plant Cell Environ. 2022. PMID: 36043225
-
SpUSP, an annexin-interacting universal stress protein, enhances drought tolerance in tomato.J Exp Bot. 2012 Sep;63(15):5593-606. doi: 10.1093/jxb/ers220. Epub 2012 Aug 21. J Exp Bot. 2012. PMID: 22915741 Free PMC article.
-
Transcription Factors Interact with ABA through Gene Expression and Signaling Pathways to Mitigate Drought and Salinity Stress.Biomolecules. 2021 Aug 5;11(8):1159. doi: 10.3390/biom11081159. Biomolecules. 2021. PMID: 34439825 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Mechanism of Stomatal Closure in Plants Exposed to Drought and Cold Stress.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2018;1081:215-232. doi: 10.1007/978-981-13-1244-1_12. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2018. PMID: 30288712 Review.
References
-
- Han J., Zhang A., Kang Y., Han J., Yang B., Hussain Q., Wang X., Zhang M., Khan M.A. Biochar promotes soil organic carbon sequestration and reduces net global warming potential in apple orchard: A two-year study in the Loess Plateau of China. Sci. Total Environ. 2022;803:150035. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.150035. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

