MicroRNAs Associated with Metformin Treatment in the Diabetes Prevention Program
- PMID: 38891870
- PMCID: PMC11172132
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms25115684
MicroRNAs Associated with Metformin Treatment in the Diabetes Prevention Program
Abstract
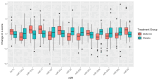
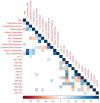
The Diabetes Prevention Program (DPP) randomized controlled trial demonstrated that metformin treatment reduced progression to type 2 diabetes (T2D) by 31% compared to placebo in adults with prediabetes. Circulating micro-ribonucleic acids (miRs) are promising biomarkers of T2D risk, but little is known about their associations with metformin regimens for T2D risk reduction. We compared the change in 24 circulating miRs from baseline to 2 years in a subset from DPP metformin intervention (n = 50) and placebo (n = 50) groups using Wilcoxon signed rank tests. Spearman correlations were used to evaluate associations between miR change and baseline clinical characteristics. Multiple linear regression was used to adjust for covariates. The sample was 73% female, 17% Black, 13% Hispanic, and 50 ± 11 years. Participants were obese, normotensive, prediabetic, and dyslipidemic. Change in 12 miR levels from baseline to 2 years was significantly different in the metformin group compared with placebo after adjusting for multiple comparisons: six (let-7c-5p, miR-151a-3p, miR-17-5p, miR-20b-5p, miR-29b-3p, and miR-93-5p) were significantly upregulated and six (miR-130b-3p, miR-22-3p, miR-222-3p, miR-320a-3p, miR-320c, miR-92a-3p) were significantly downregulated in the metformin group. These miRs help to explain how metformin is linked to T2D risk reduction, which may lead to novel biomarkers, therapeutics, and precision health strategies.
Keywords: diabetes prevention program; diabetes risk; metformin; microRNA; post-transcription.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Update of
-
MicroRNAs Associated with Metformin Treatment in the Diabetes Prevention Program.Res Sq [Preprint]. 2024 Jan 16:rs.3.rs-3846347. doi: 10.21203/rs.3.rs-3846347/v1. Res Sq. 2024. Update in: Int J Mol Sci. 2024 May 23;25(11):5684. doi: 10.3390/ijms25115684. PMID: 38313262 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
References
-
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention . National Diabetes Statistics Report, 2020. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, U.S. Department of Health and Human Services; Atlanta, GA, USA: 2020.
-
- Aroda V.R., Knowler W.C., Crandall J.P., Perreault L., Edelstein S.L., Jeffries S.L., Molitch M.E., Pi-Sunyer X., Darwin C., Heck-man-Stoddard B.M., et al. Metformin for diabetes prevention: Insights gained from the Diabetes Prevention Program/Diabetes Prevention Program Outcomes Study. Diabetologia. 2017;60:1601–1611. doi: 10.1007/s00125-017-4361-9. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Diabetes Prevention Program Research Group Long-term Effects of Metformin on Diabetes Prevention: Identification of Subgroups That Benefited Most in the Diabetes Prevention Program and Diabetes Prevention Program Outcomes Study. Diabetes Care. 2019;42:601–608. doi: 10.2337/dc18-1970. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Knowler W.C., Barrett-Connor E., Fowler S.E., Hamman R.F., Lachin J.M., Walker E.A., Nathan D.M., Diabetes Prevention Program Research Group Reduction in the incidence of type 2 diabetes with lifestyle intervention or metformin. N. Engl. J. Med. 2002;346:393–403. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa012512. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Madsen K.S., Chi Y., Metzendorf M.-I., Richter B., Hemmingsen B. Metformin for prevention or delay of type 2 diabetes mellitus and its associated complications in persons at increased risk for the development of type 2 diabetes mellitus. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2019;12:CD008558. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD008558.pub2. - DOI - PMC - PubMed

