Exploratory Untargeted Metabolomics of Dried Blood Spot Samples from Newborns with Maple Syrup Urine Disease
- PMID: 38891907
- PMCID: PMC11171634
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms25115720
Exploratory Untargeted Metabolomics of Dried Blood Spot Samples from Newborns with Maple Syrup Urine Disease
Abstract
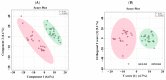
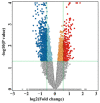
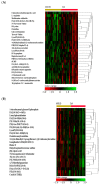
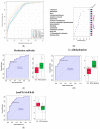
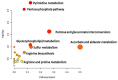
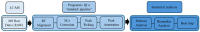
Currently, tandem mass spectrometry-based newborn screening (NBS), which examines targeted biomarkers, is the first approach used for the early detection of maple syrup urine disease (MSUD) in newborns, followed by confirmatory genetic mutation tests. However, these diagnostic approaches have limitations, demanding the development of additional tools for the diagnosis/screening of MUSD. Recently, untargeted metabolomics has been used to explore metabolic profiling and discover the potential biomarkers/pathways of inherited metabolic diseases. Thus, we aimed to discover a distinctive metabolic profile and biomarkers/pathways for MSUD newborns using untargeted metabolomics. Herein, untargeted metabolomics was used to analyze dried blood spot (DBS) samples from 22 MSUD and 22 healthy control newborns. Our data identified 210 altered endogenous metabolites in MSUD newborns and new potential MSUD biomarkers, particularly L-alloisoleucine, methionine, and lysoPI. In addition, the most impacted pathways in MSUD newborns were the ascorbate and aldarate pathways and pentose and glucuronate interconversions, suggesting that oxidative and detoxification events may occur in early life. Our approach leads to the identification of new potential biomarkers/pathways that could be used for the early diagnosis/screening of MSUD newborns but require further validation studies. Our untargeted metabolomics findings have undoubtedly added new insights to our understanding of the pathogenicity of MSUD, which helps us select the appropriate early treatments for better health outcomes.
Keywords: LysoPI; genetic testing; inborn errors of metabolism (IEMs); liquid chromatography high-resolution mass spectrometry; maple syrup urine disease (MSUD); methionine sulfoxide; newborn screening alloisoleucine; untargeted metabolomics.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Second-tier test for quantification of alloisoleucine and branched-chain amino acids in dried blood spots to improve newborn screening for maple syrup urine disease (MSUD).Clin Chem. 2008 Mar;54(3):542-9. doi: 10.1373/clinchem.2007.098434. Epub 2008 Jan 4. Clin Chem. 2008. PMID: 18178665
-
Maple syrup urine disease: further evidence that newborn screening may fail to identify variant forms.Mol Genet Metab. 2010 Jun;100(2):136-42. doi: 10.1016/j.ymgme.2009.11.010. Epub 2009 Dec 5. Mol Genet Metab. 2010. PMID: 20307994
-
Newborn screening of maple syrup urine disease and the effect of early diagnosis.Clin Chim Acta. 2023 Aug 1;548:117483. doi: 10.1016/j.cca.2023.117483. Epub 2023 Jul 6. Clin Chim Acta. 2023. PMID: 37421976
-
[Maple syrup urine disease of neonates: report of two cases and review of literature].Zhonghua Er Ke Za Zhi. 2010 Sep;48(9):680-4. Zhonghua Er Ke Za Zhi. 2010. PMID: 21092528 Review. Chinese.
-
Neonatal maple syrup urine disease in China: two novel mutations in the BCKDHB gene and literature review.J Pediatr Endocrinol Metab. 2021 Jun 30;34(9):1147-1156. doi: 10.1515/jpem-2020-0746. Print 2021 Sep 27. J Pediatr Endocrinol Metab. 2021. PMID: 34187135 Review.
Cited by
-
Metabolic profile changes in patients with rheumatoid arthritis detected using mass spectrometry.Sci Rep. 2025 Aug 7;15(1):28887. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-12994-5. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40774977 Free PMC article.
-
The MDA-MB-231 Breast Cancer Cell Secretomes Modify Metabolomes of Pseudomonas aeruginosa Breast Microbiome.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 May 22;26(11):5003. doi: 10.3390/ijms26115003. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 40507816 Free PMC article.
References
-
- IEMbase Inborn Errors of Metabolism Knowledgebase. [(accessed on 2 December 2022)]. Available online: http://www.iembase.org/
-
- Pontoizeau C., Simon-Sola M., Gaborit C., Nguyen V., Rotaru I., Tual N., Colella P., Girard M., Biferi M.G., Arnoux J.B., et al. Neonatal gene therapy achieves sustained disease rescue of maple syrup urine disease in mice. Nat. Commun. 2022;13:3278. doi: 10.1038/s41467-022-30880-w. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Imtiaz F., Al-Mostafa A., Allam R., Ramzan K., Al-Tassan N., Tahir A.I., Al-Numair N.S., Al-Hamed M.H., Al-Hassnan Z., Al-Owain M., et al. Twenty novel mutations in BCKDHA, BCKDHB and DBT genes in a cohort of 52 Saudi Arabian patients with maple syrup urine disease. Mol. Genet. Metab. Rep. 2017;11:17–23. doi: 10.1016/j.ymgmr.2017.03.006. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

