Inflammatory Cytokine-Induced Muscle Atrophy and Weakness Can Be Ameliorated by an Inhibition of TGF-β-Activated Kinase-1
- PMID: 38891908
- PMCID: PMC11172090
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms25115715
Inflammatory Cytokine-Induced Muscle Atrophy and Weakness Can Be Ameliorated by an Inhibition of TGF-β-Activated Kinase-1
Abstract
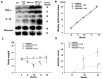
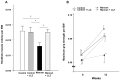
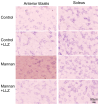
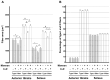
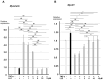
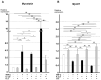
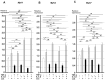
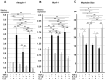
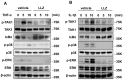
Chronic inflammation causes muscle wasting. Because most inflammatory cytokine signals are mediated via TGF-β-activated kinase-1 (TAK1) activation, inflammatory cytokine-induced muscle wasting may be ameliorated by the inhibition of TAK1 activity. The present study was undertaken to clarify whether TAK1 inhibition can ameliorate inflammation-induced muscle wasting. SKG/Jcl mice as an autoimmune arthritis animal model were treated with a small amount of mannan as an adjuvant to enhance the production of TNF-α and IL-1β. The increase in these inflammatory cytokines caused a reduction in muscle mass and strength along with an induction of arthritis in SKG/Jcl mice. Those changes in muscle fibers were mediated via the phosphorylation of TAK1, which activated the downstream signaling cascade via NF-κB, p38 MAPK, and ERK pathways, resulting in an increase in myostatin expression. Myostatin then reduced the expression of muscle proteins not only via a reduction in MyoD1 expression but also via an enhancement of Atrogin-1 and Murf1 expression. TAK1 inhibitor, LL-Z1640-2, prevented all the cytokine-induced changes in muscle wasting. Thus, TAK1 inhibition can be a new therapeutic target of not only joint destruction but also muscle wasting induced by inflammatory cytokines.
Keywords: IL-1β; MyoD1; TAK1 inhibitor; TNF-α; myostatin.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
TAK1 signaling activity links the mast cell cytokine response and degranulation in allergic inflammation.J Leukoc Biol. 2020 Apr;107(4):649-661. doi: 10.1002/JLB.2A0220-401RRR. Epub 2020 Feb 28. J Leukoc Biol. 2020. PMID: 32108376
-
RANKL Mediates Muscle Atrophy and Dysfunction in a Cigarette Smoke-induced Model of Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease.Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 2021 May;64(5):617-628. doi: 10.1165/rcmb.2020-0449OC. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 2021. PMID: 33689672
-
Joint inflammation alters gene and protein expression and leads to atrophy in the tibialis anterior muscle in rats.Am J Phys Med Rehabil. 2011 Nov;90(11):930-9. doi: 10.1097/PHM.0b013e31822dea3c. Am J Phys Med Rehabil. 2011. PMID: 21959222
-
TAK1-TABs Complex: A Central Signalosome in Inflammatory Responses.Front Immunol. 2021 Jan 5;11:608976. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2020.608976. eCollection 2020. Front Immunol. 2021. PMID: 33469458 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Molecular mechanisms and signaling pathways of angiotensin II-induced muscle wasting: potential therapeutic targets for cardiac cachexia.Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2013 Oct;45(10):2322-32. doi: 10.1016/j.biocel.2013.05.035. Epub 2013 Jun 13. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2013. PMID: 23769949 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Muscle in Endocrinology: From Skeletal Muscle Hormone Regulation to Myokine Secretion and Its Implications in Endocrine-Metabolic Diseases.J Clin Med. 2025 Jun 25;14(13):4490. doi: 10.3390/jcm14134490. J Clin Med. 2025. PMID: 40648864 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Muscle-homing peptides modified biomimetic curcumin nanoparticles ameliorate skeletal muscle dysfunction in aging mice.Redox Biol. 2025 Jul;84:103679. doi: 10.1016/j.redox.2025.103679. Epub 2025 May 14. Redox Biol. 2025. PMID: 40412023 Free PMC article.
-
Why muscle strengthening exercises should target the quadriceps and gluteus maximus in patients with knee osteoarthritis?: Effects of knee pain on muscle volume and fatty degeneration based on AI-assisted cross-sectional analysis.J Orthop Translat. 2025 Jun 28;53:221-230. doi: 10.1016/j.jot.2025.06.013. eCollection 2025 Jul. J Orthop Translat. 2025. PMID: 40678613 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Hata H., Sakaguchi N., Yoshitomi H., Iwakura Y., Sekikawa K., Azuma Y., Kanai C., Moriizumi E., Nomura T., Nakamura T., et al. Distinct contribution of IL-6, TNF-alpha, IL-1, and IL-10 to T cell-mediated spontaneous autoimmune arthritis in mice. J. Clin. Investig. 2004;114:582–588. doi: 10.1172/JCI21795. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

