The Use of Compounds Derived from Cannabis sativa in the Treatment of Epilepsy, Painful Conditions, and Neuropsychiatric and Neurodegenerative Disorders
- PMID: 38891938
- PMCID: PMC11171823
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms25115749
The Use of Compounds Derived from Cannabis sativa in the Treatment of Epilepsy, Painful Conditions, and Neuropsychiatric and Neurodegenerative Disorders
Abstract
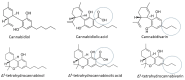
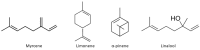
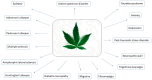
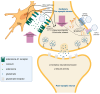
Neurological disorders present a wide range of symptoms and challenges in diagnosis and treatment. Cannabis sativa, with its diverse chemical composition, offers potential therapeutic benefits due to its anticonvulsive, analgesic, anti-inflammatory, and neuroprotective properties. Beyond cannabinoids, cannabis contains terpenes and polyphenols, which synergistically enhance its pharmacological effects. Various administration routes, including vaporization, oral ingestion, sublingual, and rectal, provide flexibility in treatment delivery. This review shows the therapeutic efficacy of cannabis in managing neurological disorders such as epilepsy, neurodegenerative diseases, neurodevelopmental disorders, psychiatric disorders, and painful pathologies. Drawing from surveys, patient studies, and clinical trials, it highlights the potential of cannabis in alleviating symptoms, slowing disease progression, and improving overall quality of life for patients. Understanding the diverse therapeutic mechanisms of cannabis can open up possibilities for using this plant for individual patient needs.
Keywords: Cannabis sativa; cannabidiol; cannabis; neurological disorders; tetrahydrocannabinol.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript; or in the decision to publish the results.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Cannabis sativa: Much more beyond Δ9-tetrahydrocannabinol.Pharmacol Res. 2020 Jul;157:104822. doi: 10.1016/j.phrs.2020.104822. Epub 2020 Apr 23. Pharmacol Res. 2020. PMID: 32335286 Review.
-
Current and Potential Use of Biologically Active Compounds Derived from Cannabis sativa L. in the Treatment of Selected Diseases.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Nov 27;25(23):12738. doi: 10.3390/ijms252312738. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39684447 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Unveiling the Potential of Phytocannabinoids: Exploring Marijuana's Lesser-Known Constituents for Neurological Disorders.Biomolecules. 2024 Oct 13;14(10):1296. doi: 10.3390/biom14101296. Biomolecules. 2024. PMID: 39456229 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cannabidiol: pharmacology and potential therapeutic role in epilepsy and other neuropsychiatric disorders.Epilepsia. 2014 Jun;55(6):791-802. doi: 10.1111/epi.12631. Epub 2014 May 22. Epilepsia. 2014. PMID: 24854329 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Therapeutic effects of cannabinoids in animal models of seizures, epilepsy, epileptogenesis, and epilepsy-related neuroprotection.Epilepsy Behav. 2017 May;70(Pt B):319-327. doi: 10.1016/j.yebeh.2016.11.006. Epub 2017 Feb 9. Epilepsy Behav. 2017. PMID: 28190698 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Psychoactive Plant Database: a phytochemical resource for neurological drug discovery.Front Pharmacol. 2025 May 23;16:1569127. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2025.1569127. eCollection 2025. Front Pharmacol. 2025. PMID: 40487401 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Full-spectrum Cannabis sativa extract enhances gut-peripheral organ integrity after experimental ischemic stroke.Inflammopharmacology. 2025 Jun;33(6):3279-3305. doi: 10.1007/s10787-025-01775-1. Epub 2025 May 19. Inflammopharmacology. 2025. PMID: 40389682
-
Harnessing Cannabis sativa Oil for Enhanced Skin Wound Healing: The Role of Reactive Oxygen Species Regulation.Pharmaceutics. 2024 Sep 30;16(10):1277. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics16101277. Pharmaceutics. 2024. PMID: 39458608 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

