Rethinking the Esterquats: Synthesis, Stability, Ecotoxicity and Applications of Esterquats Incorporating Analogs of Betaine or Choline as the Cation in Their Structure
- PMID: 38891947
- PMCID: PMC11171562
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms25115761
Rethinking the Esterquats: Synthesis, Stability, Ecotoxicity and Applications of Esterquats Incorporating Analogs of Betaine or Choline as the Cation in Their Structure
Abstract
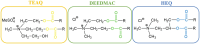
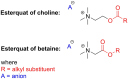
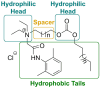
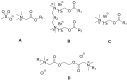
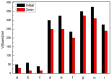
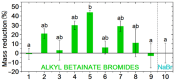
Esterquats constitute a unique group of quaternary ammonium salts (QASs) that contain an ester bond in the structure of the cation. Despite the numerous advantages of this class of compounds, only two mini-reviews discuss the subject of esterquats: the first one (2007) briefly summarizes their types, synthesis, and structural elements required for a beneficial environmental profile and only briefly covers their applications whereas the second one only reviews the stability of selected betaine-type esterquats in aqueous solutions. The rationale for writing this review is to critically reevaluate the relevant literature and provide others with a "state-of-the-art" snapshot of choline-type esterquats and betaine-type esterquats. Hence, the first part of this survey thoroughly summarizes the most important scientific reports demonstrating effective synthesis routes leading to the formation of both types of esterquats. In the second section, the susceptibility of esterquats to hydrolysis is explained, and the influence of various factors, such as the pH, the degree of salinity, or the temperature of the solution, was subjected to thorough analysis that includes quantitative components. The next two sections refer to various aspects associated with the ecotoxicity of esterquats. Consequently, their biodegradation and toxic effects on microorganisms are extensively analyzed as crucial factors that can affect their commercialization. Then, the reported applications of esterquats are briefly discussed, including the functionalization of macromolecules, such as cotton fabric as well as their successful utilization on a commercial scale. The last section demonstrates the most essential conclusions and reported drawbacks that allow us to elucidate future recommendations regarding the development of these promising chemicals.
Keywords: biological activity; cationic surfactants; cleavable compounds; environmental safety; esters; quaternary ammonium salts.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures










Similar articles
-
Esterquats: the novel class of cationic fabric softeners.J Oleo Sci. 2007;56(6):269-76. doi: 10.5650/jos.56.269. J Oleo Sci. 2007. PMID: 17898491 Review.
-
Toward revealing the role of the cation in the phytotoxicity of the betaine-based esterquats comprising dicamba herbicide.Sci Total Environ. 2022 Nov 1;845:157181. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2022.157181. Epub 2022 Jul 9. Sci Total Environ. 2022. PMID: 35817095
-
Cationic ester-containing gemini surfactants: chemical hydrolysis and biodegradation.J Colloid Interface Sci. 2007 Aug 15;312(2):444-52. doi: 10.1016/j.jcis.2007.03.044. Epub 2007 Mar 27. J Colloid Interface Sci. 2007. PMID: 17481647
-
Biological activity of quaternary ammonium salts and resistance of microorganisms to these compounds.World J Microbiol Biotechnol. 2021 Jan 11;37(2):22. doi: 10.1007/s11274-020-02978-0. World J Microbiol Biotechnol. 2021. PMID: 33428020 Review.
-
Synthesis, characterization, antimicrobial and biofilm inhibitory studies of new esterquats.Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2016 Apr 15;26(8):1978-82. doi: 10.1016/j.bmcl.2016.03.002. Epub 2016 Mar 3. Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2016. PMID: 26965863
Cited by
-
Production of an Esterquat-Based Novel Softening Agent and Its Impact on Leather and Textile Quality.ACS Omega. 2025 Mar 3;10(9):9289-9300. doi: 10.1021/acsomega.4c09502. eCollection 2025 Mar 11. ACS Omega. 2025. PMID: 40092774 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of gabapentin on solution surface properties and micellization behavior of betaine-based surfactant ionic liquids.Sci Rep. 2025 Jan 2;15(1):28. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-83777-7. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 39747962 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Javadian S., Aghdastinat H., Tehrani-Bagha A., Gharibi H. Self-Assembled Nano Structures of Cationic Ester-Containing Gemini Surfactants: The Surfactant Structure and Salt Effects. J. Chem. Thermodyn. 2013;62:201–210. doi: 10.1016/j.jct.2013.03.008. - DOI
-
- Lundberg D., Stjerndahl M., Holmberg K. Ester-based Surfactants: Are They Stable Enough? J. Surfact Deterg. 2022;26:229–236. doi: 10.1002/jsde.12628. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

