The Characteristics and Expression Analysis of the Tomato SlRBOH Gene Family under Exogenous Phytohormone Treatments and Abiotic Stresses
- PMID: 38891968
- PMCID: PMC11171631
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms25115780
The Characteristics and Expression Analysis of the Tomato SlRBOH Gene Family under Exogenous Phytohormone Treatments and Abiotic Stresses
Abstract
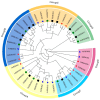
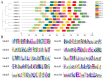
Respiratory burst oxidase homologs (RBOHs), also known as NADPH oxidases, contribute significantly to the production of ROS in plants, alongside other major sources such as photosynthesis and electron transport in chloroplasts. It has been shown that plant RBOHs play an active role in plant adversity response and electron transport. However, the phylogenetic analysis and characterization of the SlRBOH gene family in tomatoes have not been systematically studied. This study identified 11 SlRBOH genes in the tomato genome using a genome-wide search approach. The physicochemical properties, chromosomal localization, subcellular localization, secondary structure, conserved motifs, gene structure, phylogenetics, collinear relationships, cis-acting elements, evolutionary selection pressures, tissue expressions, and expression patterns under exogenous phytohormones (ABA and MeJA) and different abiotic stresses were also analyzed. We found that the SlRBOHs are distributed across seven chromosomes, collinearity reflecting their evolutionary relationships with corresponding genes in Arabidopsis thaliana and rice. Additionally, all the SlRBOH members have five conserved domains and 10 conserved motifs and have similar gene structures. In addition, the results of an evolutionary selection pressure analysis showed that SlRBOH family members evolved mainly by purifying selection, making them more structurally stable. Cis-acting element analyses showed that SlRBOHs were responsive to light, hormone, and abiotic stresses. Tissue expression analysis showed that SlRBOH family members were expressed in all tissues of tomato to varying degrees, and most of the SlRBOHs with the strongest expression were found in the roots. In addition, the expressions of tomato SlRBOH genes were changed by ABA, MeJA, dark period extension, NaCl, PEG, UV, cold, heat, and H2O2 treatments. Specifically, SlRBOH4 was highly expressed under NaCl, PEG, heat, and UV treatments, while SlRBOH2 was highly expressed under cold stress. These results provide a basis for further studies on the function of SlRBOHs in tomato.
Keywords: abiotic stress; gene family; respiratory burst oxidase; tissue expression profiling.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures









Similar articles
-
Genome-Wide Identification and Characterization of Tomato Fatty Acid β-Oxidase Family Genes KAT and MFP.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Feb 14;25(4):2273. doi: 10.3390/ijms25042273. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38396949 Free PMC article.
-
Genome-wide characterization and expression analysis of the JRL gene family in response to hormones and abiotic stress in tomato (Solanum lycopersicum L.).PeerJ. 2025 Jul 21;13:e19724. doi: 10.7717/peerj.19724. eCollection 2025. PeerJ. 2025. PMID: 40708827 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of Solanum lycopersicum L. Casein Kinase I-like Gene Family and Analysis of Abiotic Stress Response.Genes (Basel). 2025 Jun 27;16(7):757. doi: 10.3390/genes16070757. Genes (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40725413 Free PMC article.
-
Characterization of the GGP gene family in potato (Solanum tuberosum L.) and Pepper (Capsicum annuum L.) and its expression analysis under hormonal and abiotic stresses.Sci Rep. 2024 Jul 3;14(1):15329. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-66337-x. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 38961199 Free PMC article.
-
Tomato mitogen-activated protein kinase: mechanisms of adaptation in response to biotic and abiotic stresses.Front Plant Sci. 2025 Feb 3;16:1533248. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2025.1533248. eCollection 2025. Front Plant Sci. 2025. PMID: 39963529 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Antioxidant Defense Systems in Plants: Mechanisms, Regulation, and Biotechnological Strategies for Enhanced Oxidative Stress Tolerance.Life (Basel). 2025 Aug 14;15(8):1293. doi: 10.3390/life15081293. Life (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40868941 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Overexpression of OsRbohH Enhances Heat and Drought Tolerance through ROS Homeostasis and ABA Mediated Pathways in Rice (Oryza sativa L.).Plants (Basel). 2024 Sep 5;13(17):2494. doi: 10.3390/plants13172494. Plants (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39273977 Free PMC article.
-
Genome-wide identification of SlIQMs and the regulatory effect of calcium on tomato seedlings under drought stress and phytohormone treatment.Plant Cell Rep. 2025 Mar 7;44(4):70. doi: 10.1007/s00299-025-03459-0. Plant Cell Rep. 2025. PMID: 40055201
-
Genome-Wide Identification and Expression Profile Analysis of the NADPH Oxidase Gene Family in Avena sativa L.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 Mar 13;26(6):2576. doi: 10.3390/ijms26062576. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 40141217 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Du L., Jiang Z., Zhou Y., Shen L., He J., Xia X., Zhang L., Yang X. Genome-Wide Identification and Expression Analysis of Respiratory Burst Oxidase Homolog (RBOH) Gene Family in Eggplant (Solanum melongena L.) under Abiotic and Biotic Stress. Genes. 2023;14:1665. doi: 10.3390/genes14091665. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

