The Progress of the Biotechnological Production of Class IIa Bacteriocins in Various Cell Factories and Its Future Challenges
- PMID: 38891977
- PMCID: PMC11172294
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms25115791
The Progress of the Biotechnological Production of Class IIa Bacteriocins in Various Cell Factories and Its Future Challenges
Abstract
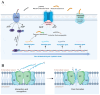
Class IIa bacteriocins produced in lactic acid bacteria are short cationic peptides with antimicrobial activity. In the search for new biopreservation agents, class IIa bacteriocins are considered to be the best potential candidates, not only due to their large abundance but also because of their high biological activity and excellent thermal stability. However, regulated by the biosynthetic regulatory system, the natural class IIa bacteriocin yield is low, and the extraction process is complicated. The biotechnological production of class IIa bacteriocins in various cell factories has been attempted to improve this situation. In this review, we focus on the application of biotechnological routes for class IIa bacteriocin production. The drawbacks and improvements in the production of class IIa bacteriocins in various cell factories are discussed. Furthermore, we present the main challenge of class IIa bacteriocins, focusing on increasing their production by constructing suitable cell factories. Recombinant bacteriocins have made considerable progress from inclusion body formation, dissolved form and low antibacterial activity to yield recovery. The development of prospective cell factories for the biotechnological production of bacteriocins is still required, which may facilitate the application of bacteriocins in the food industry.
Keywords: biotechnological production; cell factories; class IIa bacteriocin; food industry application.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The continuing story of class IIa bacteriocins.Microbiol Mol Biol Rev. 2006 Jun;70(2):564-82. doi: 10.1128/MMBR.00016-05. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev. 2006. PMID: 16760314 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Bacteriocin production and different strategies for their recovery and purification.Probiotics Antimicrob Proteins. 2014 Mar;6(1):47-58. doi: 10.1007/s12602-013-9153-z. Probiotics Antimicrob Proteins. 2014. PMID: 24676767 Review.
-
Qualitative detection of class IIa bacteriocinogenic lactic acid bacteria from traditional Chinese fermented food using a YGNGV-motif-based assay.J Microbiol Methods. 2014 May;100:121-7. doi: 10.1016/j.mimet.2014.03.006. Epub 2014 Mar 26. J Microbiol Methods. 2014. PMID: 24681304
-
Class IIa bacteriocins from lactic acid bacteria: antibacterial activity and food preservation.J Biosci Bioeng. 1999;87(6):705-16. doi: 10.1016/s1389-1723(99)80142-x. J Biosci Bioeng. 1999. PMID: 16232543
-
Maltaricin CPN, a new class IIa bacteriocin produced by Carnobacterium maltaromaticum CPN isolated from mould-ripened cheese.J Appl Microbiol. 2016 Nov;121(5):1268-1274. doi: 10.1111/jam.13248. Epub 2016 Sep 15. J Appl Microbiol. 2016. PMID: 27489131
Cited by
-
Toward safer and sustainable food preservation: a comprehensive review of bacteriocins in the food industry.Biosci Rep. 2025 Apr 17;45(4):277-302. doi: 10.1042/BSR20241594. Biosci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40259615 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Identification and Functional Analysis of Novel SNPs in Enterocin Genes of Enterococcus faecium GHB21.Probiotics Antimicrob Proteins. 2025 Feb 28. doi: 10.1007/s12602-025-10488-4. Online ahead of print. Probiotics Antimicrob Proteins. 2025. PMID: 40019734
-
The clinical praxis of bacteriocins as natural anti-microbial therapeutics.Arch Microbiol. 2024 Oct 30;206(11):451. doi: 10.1007/s00203-024-04152-8. Arch Microbiol. 2024. PMID: 39476181 Review.
-
Classification and Multi-Functional Use of Bacteriocins in Health, Biotechnology, and Food Industry.Antibiotics (Basel). 2024 Jul 18;13(7):666. doi: 10.3390/antibiotics13070666. Antibiotics (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39061348 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Yi Y., Li P., Zhao F., Zhang T., Shan Y., Wang X., Liu B., Chen Y., Zhao X., Lü X. Current status and potentiality of class II bacteriocins from lactic acid bacteria: Structure, mode of action and applications in the food industry. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2022;120:387–401. doi: 10.1016/j.tifs.2022.01.018. - DOI
-
- Fernandes S., Gomes I.B., Simoes M., Simoes L.C. Novel chemical-based approaches for biofilm cleaning and disinfection. Curr. Opin. Food Sci. 2024;55:101124. doi: 10.1016/j.cofs.2024.101124. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources