Roles of Cytokines in Alzheimer's Disease
- PMID: 38891990
- PMCID: PMC11171747
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms25115803
Roles of Cytokines in Alzheimer's Disease
Abstract
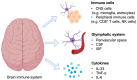
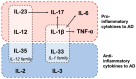
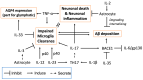
The neuroimmune system is a collection of immune cells, cytokines, and the glymphatic system that plays a pivotal role in the pathogenesis and progression of Alzheimer's disease (AD). Of particular focus are cytokines, a group of immune signaling molecules that facilitate communication among immune cells and contribute to inflammation in AD. Extensive research has shown that the dysregulated secretion of certain cytokines (IL-1β, IL-17, IL-12, IL-23, IL-6, and TNF-α) promotes neuroinflammation and exacerbates neuronal damage in AD. However, anti-inflammatory cytokines (IL-2, IL-3, IL-33, and IL-35) are also secreted during AD onset and progression, thereby preventing neuroinflammation. This review summarizes the involvement of pro- and anti-inflammatory cytokines in AD pathology and discusses their therapeutic potential.
Keywords: Alzheimer’s disease; cytokine; neuroimmune system; pro- and anti-inflammatory cytokines.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- 11102218/Research Grants Council
- PDFS2122-1S01/Research Grants Council
- 11200422/Research Grants Council
- RFS2223-1S02/Research Grants Council
- C1134-20G/Research Grants Council
- 7005433/City University of Hong Kong
- 7005626/City University of Hong Kong
- 9239070/City University of Hong Kong
- 9609307/City University of Hong Kong
- 9610560/City University of Hong Kong
- 32370959/National Natural Science Foundation of China
- 2021A1515010569/Natural Science Foundation of Guangdong province
- 2022A1515012450/Natural Science Foundation of Guangdong province
- 11.21.4621.AC.162846.00.00/Hong Kong Baptist University
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

