The Importance of Large-Scale Genomic Studies to Unravel Genetic Risk Factors for Autism
- PMID: 38892002
- PMCID: PMC11172008
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms25115816
The Importance of Large-Scale Genomic Studies to Unravel Genetic Risk Factors for Autism
Abstract
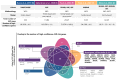
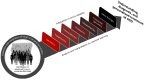
Autism spectrum disorder (ASD) is a common and highly heritable neurodevelopmental disorder. During the last 15 years, advances in genomic technologies and the availability of increasingly large patient cohorts have greatly expanded our knowledge of the genetic architecture of ASD and its neurobiological mechanisms. Over two hundred risk regions and genes carrying rare de novo and transmitted high-impact variants have been identified. Additionally, common variants with small individual effect size are also important, and a number of loci are now being uncovered. At the same time, these new insights have highlighted ongoing challenges. In this perspective article, we summarize developments in ASD genetic research and address the enormous impact of large-scale genomic initiatives on ASD gene discovery.
Keywords: autism spectrum disorder; gene discovery; genetic heterogeneity; genomic technologies; large patient cohorts; locus discovery.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Genetic architecture of autism spectrum disorder: Lessons from large-scale genomic studies.Neurosci Biobehav Rev. 2021 Sep;128:244-257. doi: 10.1016/j.neubiorev.2021.06.028. Epub 2021 Jun 21. Neurosci Biobehav Rev. 2021. PMID: 34166716 Review.
-
Whole Exome Sequencing Identifies Novel De Novo Variants Interacting with Six Gene Networks in Autism Spectrum Disorder.Genes (Basel). 2020 Dec 22;12(1):1. doi: 10.3390/genes12010001. Genes (Basel). 2020. PMID: 33374967 Free PMC article.
-
Functional DNA methylation signatures for autism spectrum disorder genomic risk loci: 16p11.2 deletions and CHD8 variants.Clin Epigenetics. 2019 Jul 16;11(1):103. doi: 10.1186/s13148-019-0684-3. Clin Epigenetics. 2019. PMID: 31311581 Free PMC article.
-
Analysis of common genetic variation and rare CNVs in the Australian Autism Biobank.Mol Autism. 2021 Feb 10;12(1):12. doi: 10.1186/s13229-020-00407-5. Mol Autism. 2021. PMID: 33568206 Free PMC article.
-
Leveraging large genomic datasets to illuminate the pathobiology of autism spectrum disorders.Neuropsychopharmacology. 2021 Jan;46(1):55-69. doi: 10.1038/s41386-020-0768-y. Epub 2020 Jul 15. Neuropsychopharmacology. 2021. PMID: 32668441 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Calcium Signaling and Molecular Adhesion Processes May Hold the Key to Genetic Risk for Autism: A Molecular Pathway Analysis on Two Independent Samples.Genes (Basel). 2024 Dec 17;15(12):1609. doi: 10.3390/genes15121609. Genes (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39766876 Free PMC article.
-
Autism Spectrum Disorder Pathogenesis-A Cross-Sectional Literature Review Emphasizing Molecular Aspects.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Oct 20;25(20):11283. doi: 10.3390/ijms252011283. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39457068 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Neurobiological basis of autism spectrum disorder: mini review.Front Psychol. 2025 May 30;16:1558081. doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2025.1558081. eCollection 2025. Front Psychol. 2025. PMID: 40519825 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A Systems Biology Approach for Prioritizing ASD Genes in Large or Noisy Datasets.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 Feb 27;26(5):2078. doi: 10.3390/ijms26052078. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 40076702 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Maenner M.J., Warren Z., Williams A.R., Amoakohene E., Bakian A.V., Bilder D.A., Durkin M.S., Fitzgerald R.T., Furnier S.M., Hughes M.M., et al. Prevalence and Characteristics of Autism Spectrum Disorder among Children Aged 8 Years-Autism and Developmental Disabilities Monitoring Network, 11 Sites, United States, 2020. MMWR Surveill Summ. 2023;72:1–14. doi: 10.15585/mmwr.ss7202a1. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

